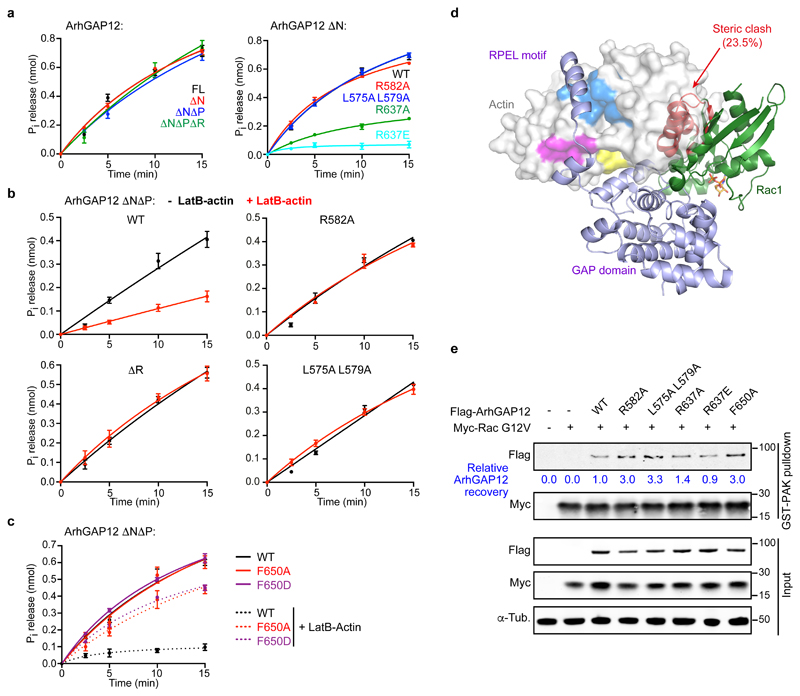
Figure 4. G-actin inhibits ArhGAP12 GAP activity by occluding rho protein binding.
GAP activity towards Rac1 was assessed using a colorimetric assay for Pi release. Data were fitted by non-linear regression; data are means ± SEM, n=3 (a left, b), n=4 (a right, c) independent experiments. (a) Effect of ArhGAP12 truncations and point mutations of the RPEL motif or catalytic R637. (b) GAP activity is suppressed by 10 μM LatB-actin, and this requires the RPEL motif. (c) Alanine or aspartate substitutions at niche contact residue F650 do not affect GAP activity, but relieve the inhibitory effect of LatB-actin. (d) Model of Rac1 bound to ArhGAP12. The GAP domain of the MgcRacGAP:Cdc42.GDP structure (PDB ID 5C2J) was superimposed onto the GAP domain of the ArhGAP12 ΔNΔP•actin structure. The Rac1 structure (PDB 5N6O) was then superimposed onto the Cdc42 model (RMSD 0.50Å, 148 Cα). Exposed and occluded Rac1 residues are shown as green and red ribbons, GDP in orange. The degree of occlusion is similar for Cdc42 (23.7%) and Rac1 (23.5%). (e) Flag-ArhGAP12 derivatives and constitutively active Myc-RacG12V were co-expressed in NIH 3T3 cells; and recovery of ArhGAP12 and Myc-RacG12V in GST-PAK CRIB pulldown assays assessed by immunoblotting. Representative immunoblots from 3 independent experiments are shown. See Supplementary Figure 3 for related data. Source data for a-c are shown in Supplementary Table 1. Unprocessed blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 8.