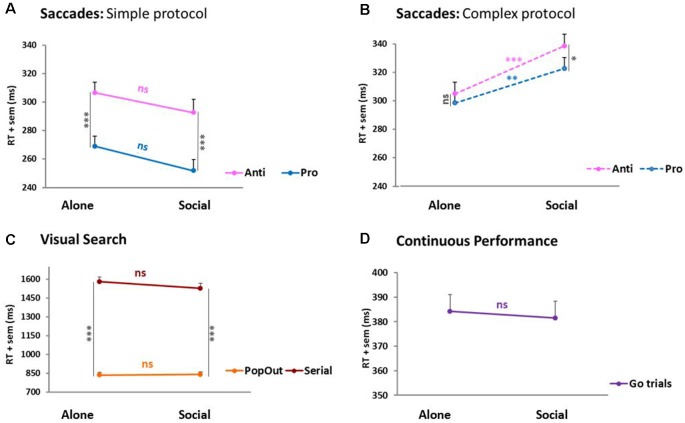
Figure 4.
Reaction times (RTs). (A) Saccades: simple Protocol. (B) Saccades: complex protocol. (C) Visual search. (D) Continuous performance. In the simple protocol where pro- and anti-saccades were tested separately, pro-saccades RTs were ~40 ms shorter than anti-saccades RTs (***p ≤ 0.005, paired t-tests). In the complex protocol, where pro- and anti-saccades were mixed pseudo-randomly, this difference across saccade types was null (ns) or marginal (*p = 0.054). However, the saccades revealed a significant social influence at the group-level. In the simple protocol, saccades (pro- and anti- alike) were slightly (~15 ms) faster under social testing (Social) than under solitary testing (Alone), though the difference failed to reach significance (ns). By contrast, in the complex protocol, saccades (again, pro- and anti- alike) were both significantly slower (~20–30 ms) under social than solitary testing (pro- **p = 0.02; anti- ***p = 0.007). The two other tasks failed to show any social effect. Visual search only showed a trial difficulty effect where Serial trials were significantly longer than PopOut trials (***p < 0.001).