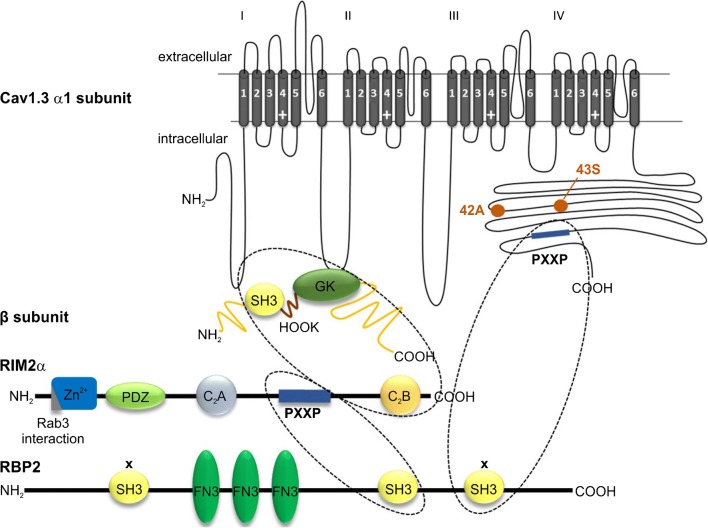
Fig. 1.
Interaction of RBP2 with Cav1.3 channels. RIMs and RBPs are multidomain proteins [41, 46]. All RIM isoforms (RIM1α and 1β; RIM2α, 2β, and 2γ; RIM3γ and RIM4γ) bind via their C2B domain to the auxiliary β subunit of the Ca2+ channel complex. Disruption of the SH3 or GK domain in the β subunit prevents the interaction with RIM [28]. All three RBP isoforms contain three SH3 domains and two (RBP3) or three (RBP1 and 2) FN3 domains [41]. The second SH3 domain of RBP binds to the proline-rich region (PXXP) present only in RIMα or β isoforms, located between the two C2 domains. The other SH3 domains, marked by “x,” in turn can interact with a proline-rich region (PXXP) localized in the full-length Cav1.3 C terminus [23]. Note that incorporation of alternative exons 42A and 43S leads to short C-terminal splice variants (Cav1.342A or Cav1.343S, respectively; C-terminal ends indicated by orange dots) lacking the PXXP interaction site. AID, α-interaction domain; FN3, fibronectin 3 domain; GK, guanylate-kinase like domain; PXXP, proline-rich region; SH3, SRC homology 3 domain; Zn2+, zinc finger domain. Note that RIM may also interact via its C2B domain with the C terminus of Cav1.3, but the interaction site is unknown [49]