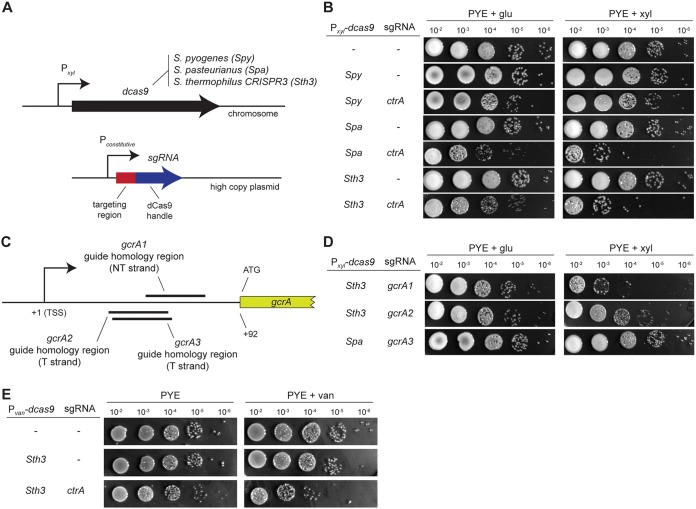
FIG 1.
CRISPRi systems to downregulate gene expression in Caulobacter crescentus. (A) Design of the different constructs used in this study. Each system consists of a nuclease-dead variant of the cas9 gene (dcas9) expressed under the control of a xylose (or vanillate) promoter and the corresponding specific single guide RNA (sgRNA) constitutively expressed (see Materials and Methods). (B) Efficiency of downregulating ctrA expression using the different CRISPRi systems from S. pyogenes, S. thermophilus CRISPR3, and S. pasteurianus. Shown are serial dilutions of each strain on PYE supplemented with 0.2% glucose or 0.3% xylose after 48 h at 30°C. Note that the commonly used S. pyogenes system is not functional in C. crescentus, although it targets the same sequence as the S. pasteurianus system here. Strand and sequence targeting of the different sgRNAs is detailed in Fig. S1A. (C) Strand and sequence targeting of the different sgRNAs for gcrA used in panel D. TSS, transcription start site; T, template; NT, nontemplate. (D) Efficiency of downregulating gcrA expression when targeting the nontemplate strand using dCas9 derived from S. thermophilus CRISPR3 and S. pasteurianus. Shown are serial dilutions of each strain on PYE supplemented with 0.2% glucose or 0.3% xylose after 48 h at 30°C. (E) Efficiency of downregulating ctrA expression with the dCas9 of S. thermophilus CRISPR3 under a vanillate-inducible promoter. Shown are serial dilutions of each strain on PYE or PYE supplemented with 500 μM vanillate after 48 h at 30°C.