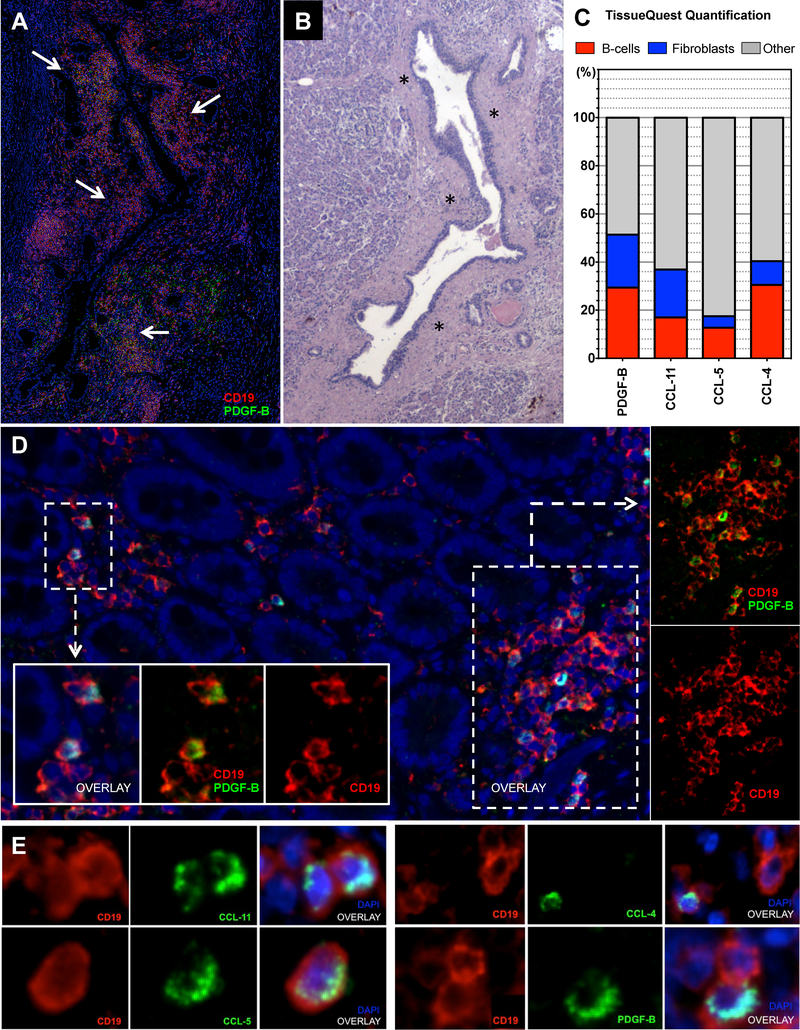
Figure 3. B-lymphocytes and fibroblasts infiltrating IgG4-RD autoimmune pancreatitis express PDGF-B, CCL-4, CCL-5, and CCL-11.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of an IgG4-RD AIP tissue, showing PDGF-B expressing B cells (arrows) surrounding pancreatic ducts (CD19 (red), PDGF-B (green), and DAPI (blue)). (B) Sequential matched Hematoxylin/Eosin stain showing a dense fibrosis (asterisks) likely generated as a consequence of the peri-ductal inflammatory infiltrate described in A. (C) Quantification of double-positive cells for CD19+ (red bars) or αSMA+ (blue bars) and CCL-4, CCL-5, CCL-11, or PDGF-B in IgG4-RD AIP expressed in percentage of total CCL-4, CCL-5, CCL-11, or PDGF-B positive cells (i.e. CD19+PDGF-B+ cells/PDGF-B+ cells). Bar length represents the average quantification of 5 tissue slides. (D) PDGF-B expressing B lymphocytes infiltrating the sub-epithelial layer of the duodenum in a case of IgG4-RD AIP of the pancreatic head (low magnification); inserts (high magnification). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of CD19 (red), CCL-4, CCL-5, CCL-11, and PDGF-B (all green), and DAPI (blue) positive cells in representative tissue samples from a patient with IgG4-RD AIP (high magnification).