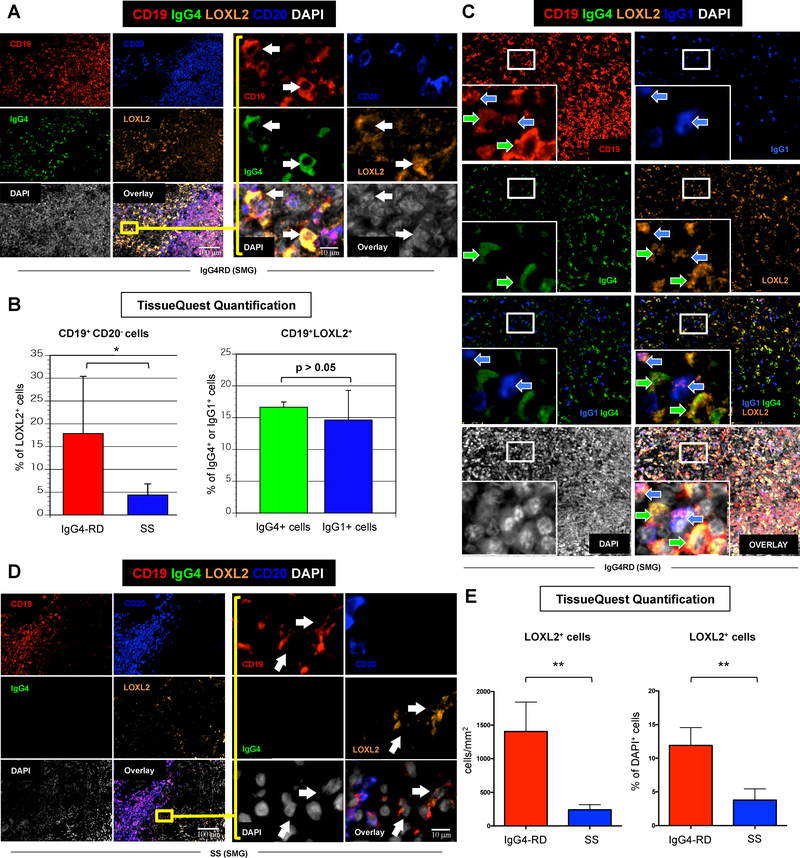
Figure 5. LOXL2 is highly expressed by plasmablasts/plasma cells in IgG4-related sialoadenitis.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of CD19 (red), IgG4 (green), LOXL-2 (orange), CD20 (blue), and DAPI (white) in salivary glands from a representative patient with IgG4-RD showing abundant infiltrate of LOXL2 expressing IgG4+ plasmablasts (arrows) (inserts: high magnification). (B) Quantification of LOXL2+ plasmablasts (CD19+ CD20− B cells) in salivary glands from patients with IgG4-RD (red bar) and Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) (blue bar) using TissueQuest software. * = p < 0.05 (mean ± SD of n=5 experiments). Quantification of LOXL2+ cells within the total pool IgG4+ (red bar) or IgG1+ (blue bar) plasmablasts in salivary glands from patients with IgG4-RD using TissueQuest software (mean ± SD of n=5 experiments). (C) Immunofluorescence staining of CD19 (red), IgG4 (green), LOXL-2 (orange), IgG1 (blue), DAPI (white) in the salivary gland of a representative patient with IgG4-RD showing LOXL2 expression by both IgG4 (green arrows) and IgG1 (blue arrows) producing B cells (inserts: high magnification). (D) Immunofluorescence staining of CD19 (red), IgG4 (green), LOXL-2 (orange), CD20 (blue), and DAPI (white) in salivary glands from a representative patient with SS showing few LOXL2 expressing IgG4+ B lymphocytes (arrows) (inserts: high magnification). (E) Quantification of LOXL2+ cells in salivary glands from patients with IgG4-RD (red bar) and SS (blue bar) showing a significantly lower number of LOXL2 expressing cells in SS compared to IgG4-RD. ** = p < 0.01 (mean ± SD of n=5 experiments).