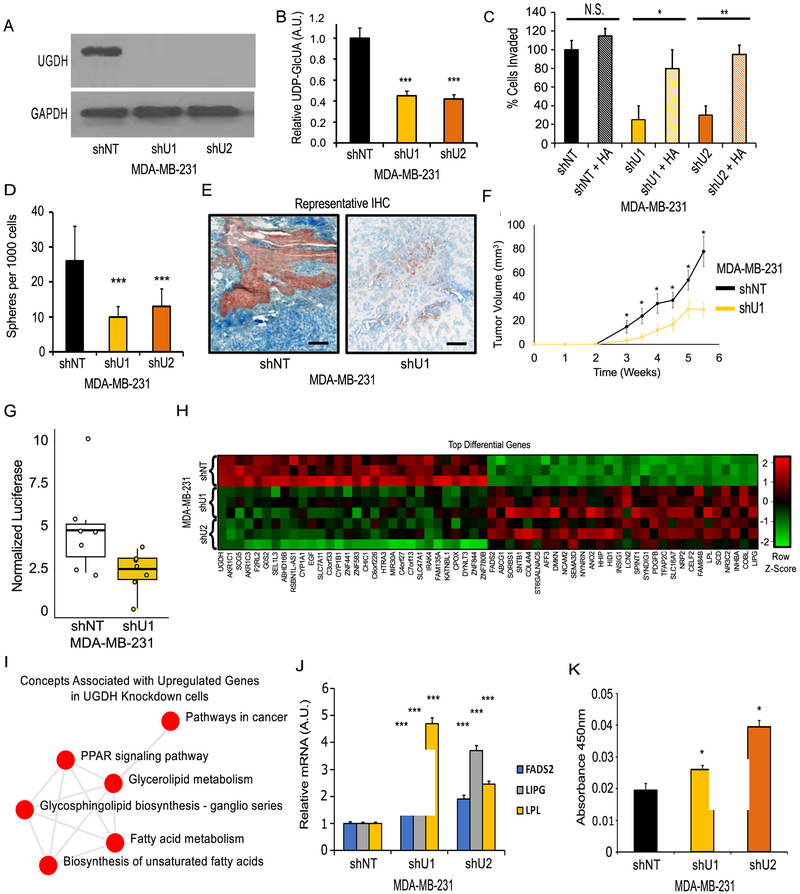
Figure 3: Effects of UGDH knockdown in a mesenchymal-like breast cancer cell line model.
A) Western blot showing shRNA-mediated knockdown (KD) of UGDH in MDA-MB-231 (M231) by two independent shRNAs (shU1, shU2) compared to non-target shRNA (shNT). B) UGDH KD reduces intracellular UDP-GlcUA. C) UGDH KD reduces cellular invasiveness in an HA-dependent manner as measured by transwell invasion assay. D) UGDH KD significantly reduces colony formation in soft agar. E) IHC of CAM models stained for UGDH (red), hyaluronic acid (Blue), with methyl green counter stain. 20X Magnification, scale bars are 50µm. F) UGDH KD tumors (shU1) in SCID-Beige mice grow at reduced rates compared to control shNT tumors (n=8). Two tumors from each cell line were removed once tumor volume of 50 mm3 was reached (4.5 weeks and 5.5 weeks post injection for shNT and shU1, respectively) to examine differences in HA levels in early stage tumors. (G) Pulmonary metastasis was reduced in UGDH KD cells compared to control shNT cells following tail-vein injection as quantified by luciferase signal. H) Heatmap of top 60 differential genes with FDR-corrected p-value <0.05, genes are ordered from lowest to greatest fold-change in UGDH KD models vs. control. I) Network of pathways associated with overexpressed genes in UGDH KD models indicates enrichment of genes involved in lipid metabolism and PPAR signaling. J) RT-PCR confirmation that FADS2, LIPG, and LPL lipid metabolism genes are upregulated following UGDH KD. K) PPAR-gamma transcription factor binding assay shows UGDH knockdown increases PPAR-gamma DNA binding activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. N.S. = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** < 0.001, versus control.