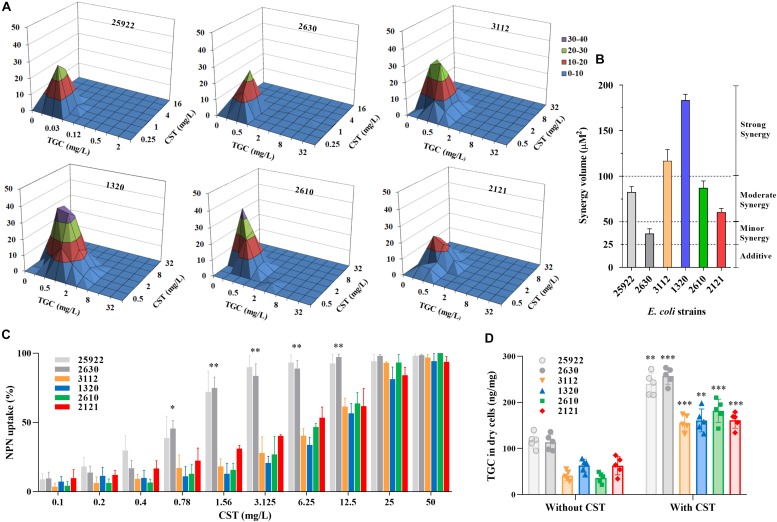
FIGURE 2.
In vitro interactions between colistin and tigecycline. (A,B) Synergism as demonstrated using MacSynergy II plots of the three-dimensional dose-response curves. The flat plane represents the predicted indifference between antagonism and synergy. Peaks and troughs represent synergy and antagonism, respectively. Synergy expressed as the calculated interaction volumes (μM2) at a confidence interval of 95%: <25, additive; 25 to 50, minor but significant; 50 to 100, moderate; and >100, strong synergy. (C) Colistin-induced NPN uptake (%) of mcr-1-positive and -negative E. coli strains. The data represents background subtracted fluorescence divided by the fluorescence observed at 100 mg/L of colistin. (D) Accumulations of tigecycline in E. coli strains (dry weight) after exposure to 10 mg/L tigecycline for 20 min in the presence and absence of colistin. Data shown are the means of five independent biological replicates. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.