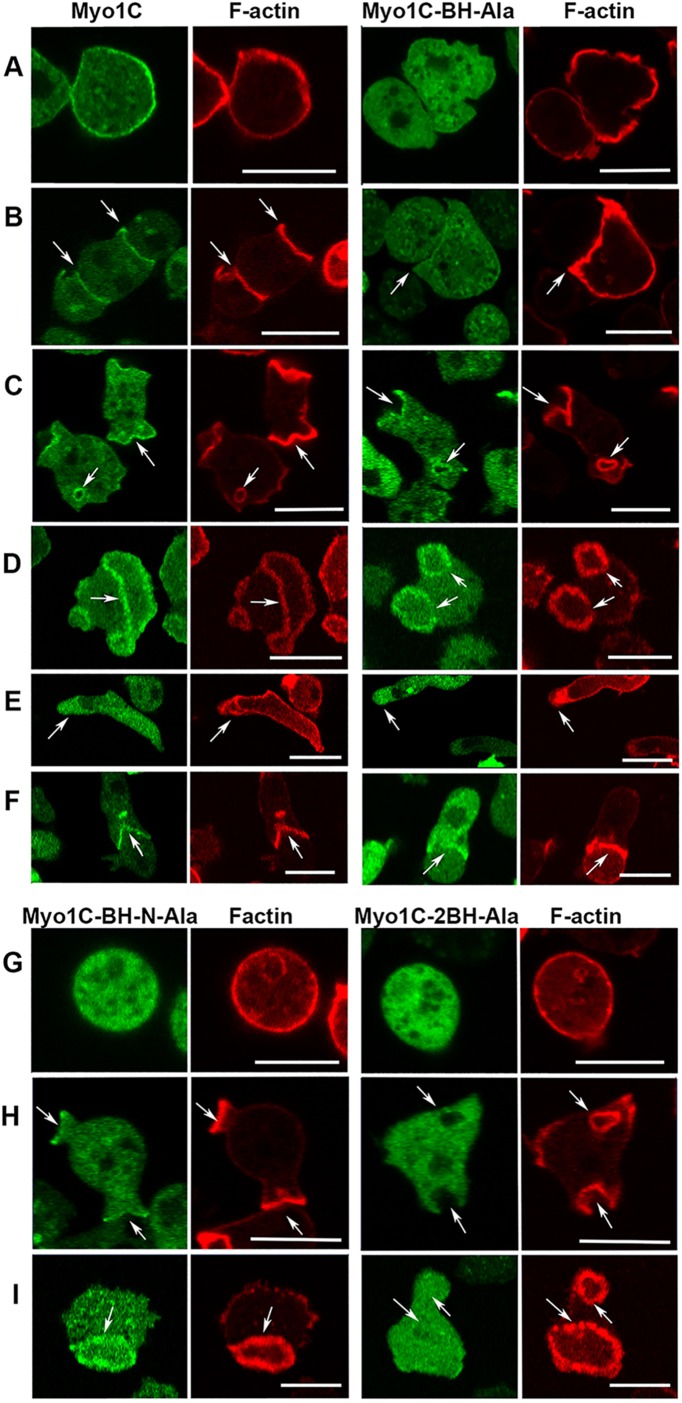
FIGURE 12:
Localization of Myo1C and its BH mutants. (A–F) Localization of Myo1C and Myo1C-BH-Ala. Myo1C localizes sharply on the plasma membrane in nonmotile cells (A), in cell–cell contacts (B), in macropinocytic protrusions and vesicles (C), together with actin in actin waves (D), diffusely at the front of elongated cells (E), and sharply at the mouth of chemotaxing cells (F). Myo1C-BH-Ala is barely detectable in plasma membrane of nonmotile cells (A) and at cell–cell contacts (B) but it is clearly present in macropinocytic protrusions and vesicles (C), in actin waves (D) at the front of chemotaxing cells (E), and it is detectable in the mouth of streaming cells (F). (G, H) Localization of Myo1C-BH-N-Ala and Myo1C-2BH-Ala mutants on the plasma membrane of nonmotile cells (G), in macropinocytic protrusions (H), and in actin waves (I). Note that mutation of both BH sites together (Myo1C-2BH-Ala) abolished membrane association of Myo1C, whereas mutations of single sites had only a partial effect. Arrows point to the regions of interest. Cells in A and G were fixed; all others are images of live cells. The same localization was observed in AX2 and Myo1B null cells. Images shown are of AX2 cells. Bars are 10 μm. The number of independent transfections was eight for Myo1C, four for Myo1C-BH-Ala, and two for Myo1C-BH-N-Ala and Myo1C-2BH-Ala. At least two independent experiments were performed for each transfection under each condition. The images are representative of more than 100 cells observed under each condition.