Fig. 3.
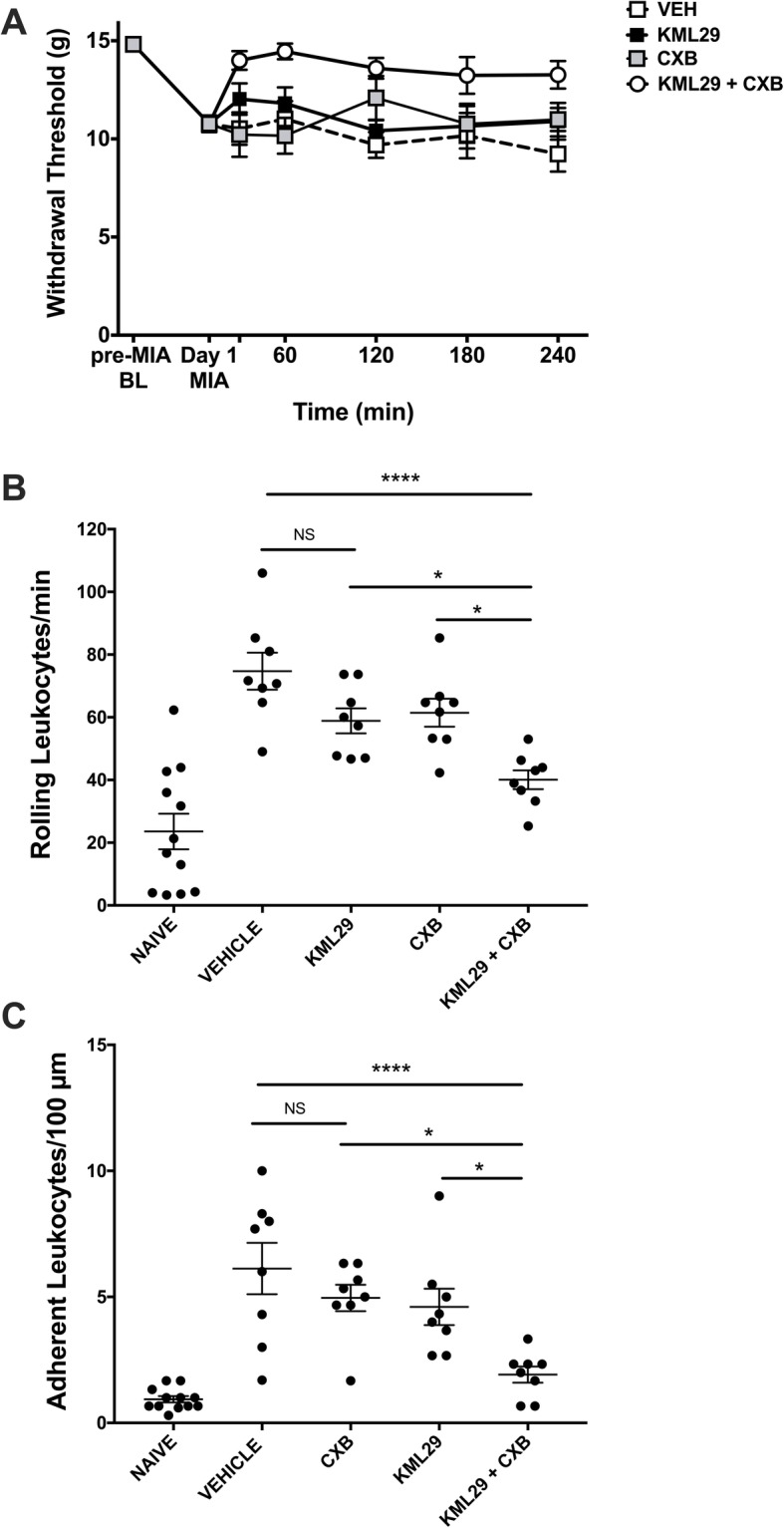
Combination of KML29 and low-dose celecoxib improves pain and inflammation on day 1 of MIA model of OA. Local administration of KML29 (700 μg) and systemic administration of CXB (3 mg/kg) significantly improved the hindpaw withdrawal threshold over a 240-min time course (a) compared to either treatment alone (P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05, ∇∇∇P < 0.001, ∇∇P < 0.01; n = 8). The KML29 and CXB combination also significantly decreased both rolling leukocytes (b) (P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; ****P < 0.0001, *P < 0.05; n = 8) and adherent leukocytes (c) (P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05; n = 8) at 360 min post-drug administration, compared to either treatment alone. Data are mean values ± SEM. ANOVA, analysis of variance; BL, baseline; CXB, celecoxib; MIA, sodium monoiodoacetate; VEH, vehicle; *post hoc comparison between KML29 + CXB and vehicle; #post hoc comparison between KML29 and KML29 + CXB; ∇post hoc comparison between CXB and KML29 + CXB
