FIGURE 7.
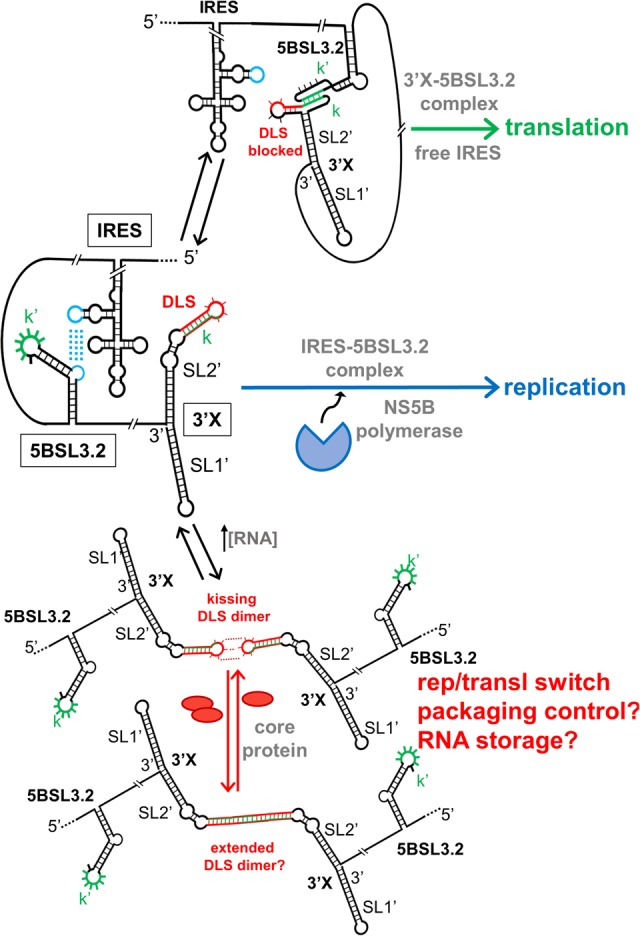
Scheme summarizing the structure and functional interactions of the 3′X domain of HCV, together with their possible impact on the virus life cycle. When the distal contact between the 3′X and 5BSL3.2 domains is established, the IRES is free and can initiate translation. In the absence of this interaction, the 5BSL3.2 domain is complexed with the IRES and synthesis of the negative-sense strand starts from the 3′X domain. At higher viral RNA concentrations, 3′X domain homodimers are formed through kissing loop contacts between palindromic DLS loops. These homodimers are involved in regulating the switch between translation and replication. They may also act as intermediary species in the process of packaging, or alternatively as a means to store virus RNA in the infected cell. For simplicity, the SL9005 domain is not shown.
