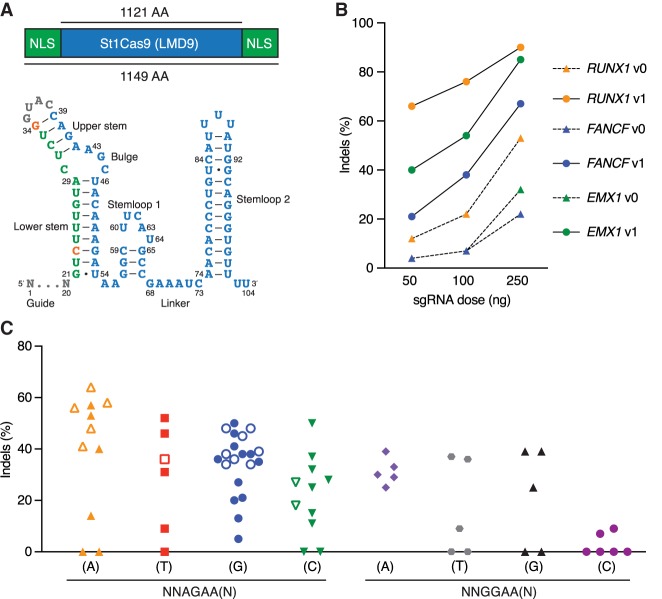
Figure 1.
Functional PAM sequences for robust and potent DNA cleavage by St1Cas9 LMD9 in mammalian cells. (A) Schematic representations of St1Cas9 LMD9 flanked by nuclear localization signals (NLSs) and its engineered sgRNA (v1). Nucleotide sequence and functional modules are depicted; crRNA (green), loop (gray), tracrRNA (blue), and mutated nucleotides (orange). (B) K562 cells stably expressing St1Cas9 were transfected with indicated sgRNA expression vectors at increasing doses, and TIDE assays were performed 3 d later to determine the frequency of indels. An expression vector encoding EGFP (−) was used as a negative control. The experiment was performed twice and yielded equivalent results; only one is shown. (C) Screening for guides targeting St1Cas9 LMD9 to various PAMs was performed by transient transfections in K562 (solid shapes) and Neuro-2a (open shapes) cells using single-vector constructs driving the expression of St1Cas9 and its sgRNA. Surveyor assays were performed 3 d later to determine the frequency of indels. An expression vector encoding EGFP (−) was used as a negative control. See also Supplemental Figure S1.