Figure 5.
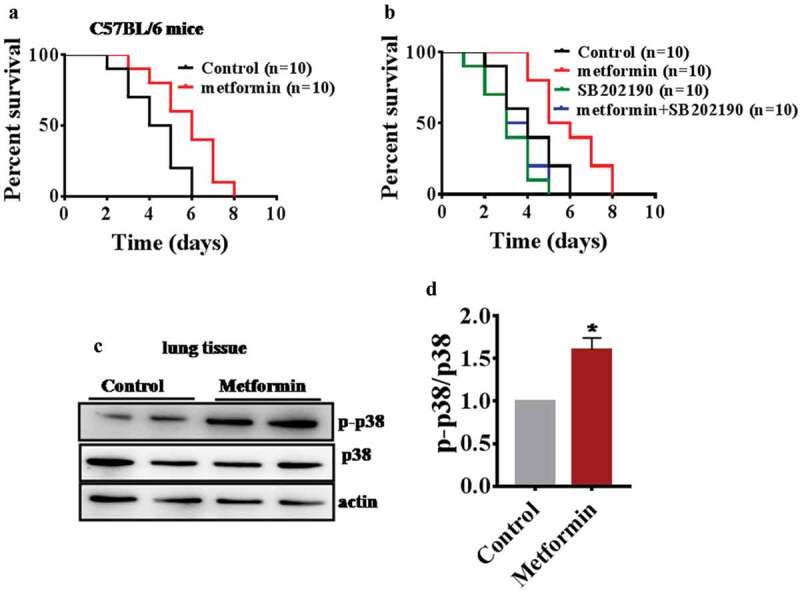
Metformin protected mice against P. aeruginosa infection and increased p-p38 in the lung.
(a) Metformin (200 mg/kg body weight) treated mice increases the resistance to P. aeruginosa PA14 infection compared with control mice. *P< 0.05 (log-rank test). (b) The p38 inhibitor SB202190 increased the susceptibility to P. aeruginosa PA14 infection compared with control mice *P< 0.05 (log-rank test) and suppressed the enhanced resistance to P. aeruginosa PA14 upon metformin (200 mg/kg body weight) treatment P =0.0512 (log-rank test). (c) Metformin (200 mg/kg body weight) significantly increased the levels of active PMK-1 in the lung. (d) The right panel shows quantification of phosphorylated p38 MAPK levels. These results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P< 0.05 versus control (one-way ANOVA followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls test).
