Figure 4.
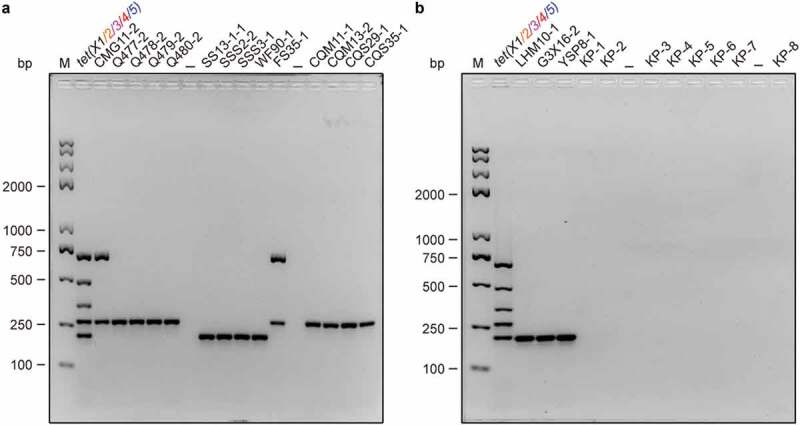
The use of multiplex PCR to screen tet(X) variants in field/clinical isolates. The stains examined here include field isolates and clinical isolates. All the field isolates were provided by the collaborator Dr. Jian Sun from South China Agriculture University, Guangzhou, China (Table 2). Among them, 17 are detected to be positive for tet(X) variants, including 8 tet(X5)-positive Acinetobacter isolates (Q477-2, Q478-2, Q479-2, Q480-2, CQW11-1, CQW13-2, CQS29-1 & CQS35-1), and 7 tetX4-bearing E. coli isolates (LHM10-1, G3X16-2, YSP8-1, SS13-1-1, SSS2-2, SSS3-1 & WF90-1), and 2 Acinetobacter isolates coharboring tet(X3) and tet(X5) (Table 2). The remaining eight strains (KP-1 to KP-8) refer to clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae with tigecycline resistance, collected from The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine. Electrophoresis of 2% agarose gel was applied to separate the mixture of PCR products. Designations: bp, base pair; M, DNA marker (Trans 2K Plus II); the symbol “–”, negative control; the mixture of tet(X) [X1 to X5] PCR products, positive control.
