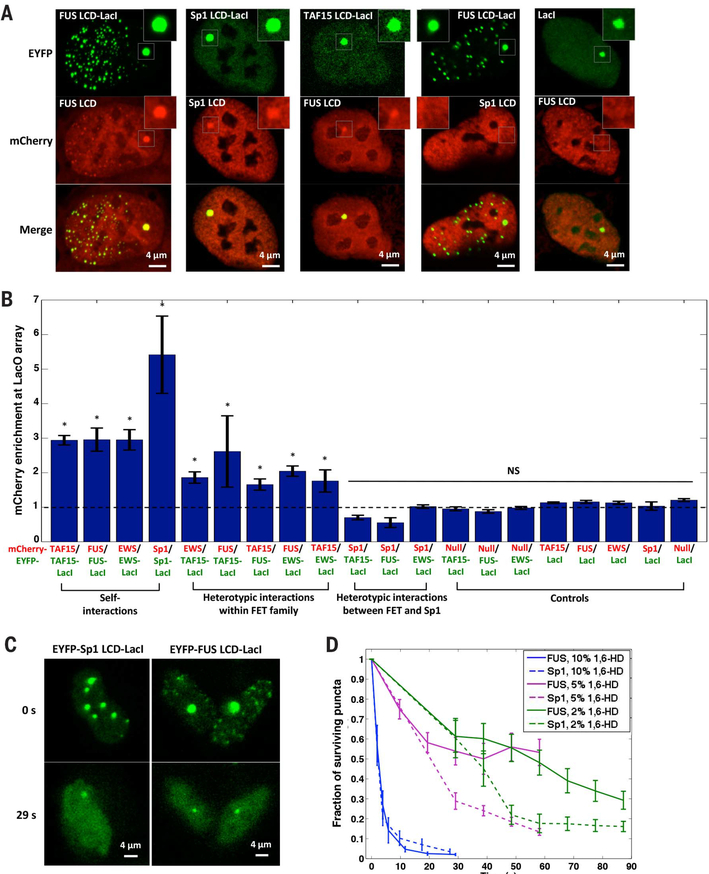
Fig. 2. LCD hub formation involves selective protein-protein interactions, which can be disrupted by 1,6-HD with sequence-dependent sensitivity.
(A) Confocal fluorescence images of U2OS cells containing LacO array 1 that coexpress various combinations of mCherry-LCD and EYFP-LCD-LacI. The region surrounding the LacO array is zoomed in.
(B) Quantification of the enrichment of mCherry-LCD (red) at the LacO array 1 bound by various EYFP-labeled LCD-LacI fusion proteins (green), calculated as the peak mCherry fluorescence intensity at the array divided by the average intensity immediately surrounding the array (fig. S5A). Null, mCherry not fused to any LCD. An mCherry enrichment at the array above 1 suggests LCD-LCD interactions. * denotes a statistically significant difference above 1 (P < 0.05, one-sample t test). NS, nonsignificant difference above 1. Error bars represent SE. (C) Fluorescence images of FUS and Sp1 LCD hubs before (0 s) and after (29 s) addition of 10% 1,6-HD.
(D) Number of nuclear puncta formed by FUS or Sp1 LCD surviving over time upon addition of 1,6-HD at different concentrations. Error bars represent SE.