Figure 1.
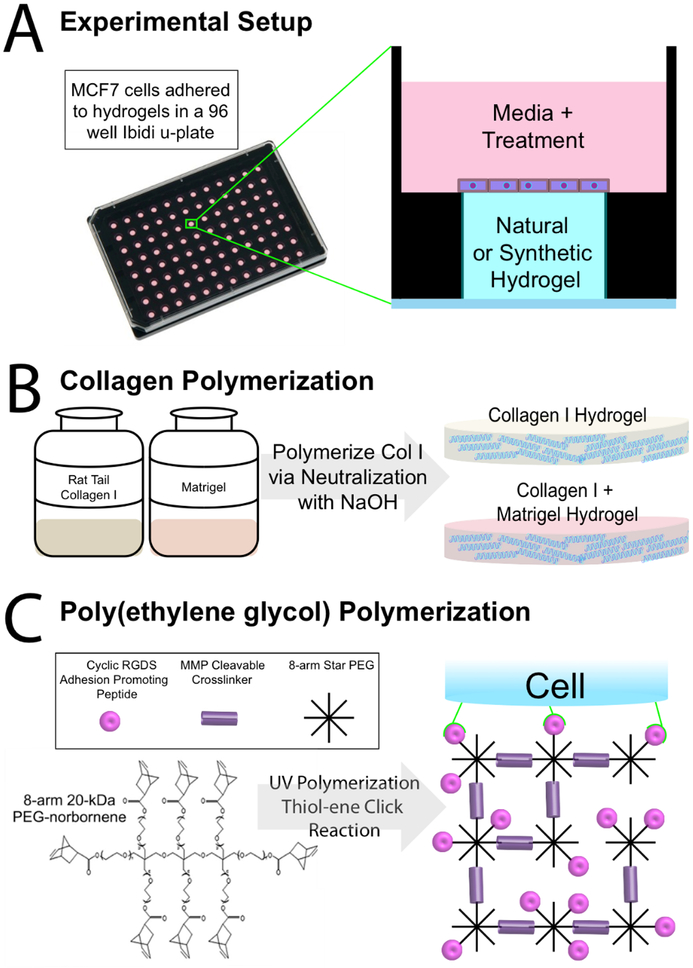
Experimental and Hydrogel Overview A. Side-view schematic of 2D cells on hydrogel culture in Ibidi 96 μ-plate, which are optimal for flat topography of hydrogels allowing for facile optical analysis. ER+ breast cancer tissue models on each of the different hydrogels are subject to 4 concentrations of E2 (17-β estradiol) or vehicle. B. Col I and col I + Matrigel are polymerized to a 4mg/mL col I concentration and a 4mg/mL col I + 2mg/mL Matrigel concentration. C. Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) (50mg/mL) hydrogel made by UV crosslinking 60% of arms of 8-arm star PEG monomers with an MMP cleavable cross-linker, and incorporating 6mM and 8mM concentrations of CycRGDS adhesion-promoting peptide (PEG6 and PEG8, respectively).