Figure 2.
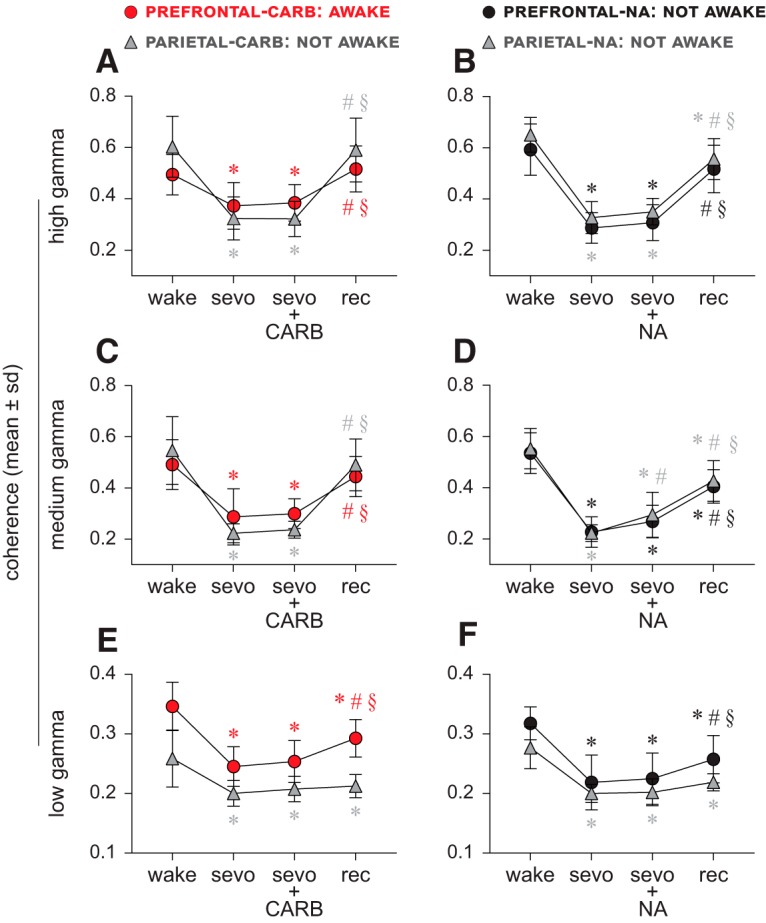
Corticocortical coherence does not correlate with level of consciousness. A–F, Sevoflurane anesthesia (sevo) significantly reduced corticocortical coherence in high (125–155 Hz), medium (85–125 Hz), and low (25–55 Hz) gamma range. Cholinergic stimulation of PFC through reverse dialysis delivery of 5 mm carbachol (CARB) was reported to induce wakefulness in the presence of sevoflurane anesthesia (Pal et al., 2018) but failed to restore gamma coherence (high, medium, low) to baseline wake levels (A,C,E). Similar delivery of CARB into parietal cortex or 20 mm NA into prefrontal and parietal cortices during sevoflurane anesthesia did not restore wakefulness (Pal et al., 2018), and none of these interventions restored disrupted gamma coherence (A–F). The gamma coherence during the post-sevoflurane recovery wake epoch (rec) showed a trend toward return to baseline wake levels (A–F) but remained significantly low, except in the high and medium gamma bands for prefrontal- and parietal cortex-CARB (A) and prefrontal-NA (B) groups. A linear mixed model with random intercept for each rat was used for the statistical comparisons, and the post hoc pairwise tests were single-step corrected for multiple comparisons. The statistical comparisons are shown at p < 0.05. The mean, SD, exact p values, F statistics, and the effect sizes for each statistical comparison are provided in Tables 1 and 2. The significance symbols are color-coded to match the line-symbol plots. *Significant compared with baseline wake state. #Significant compared with sevo. §Significant compared with CARB or NA during sevo.
