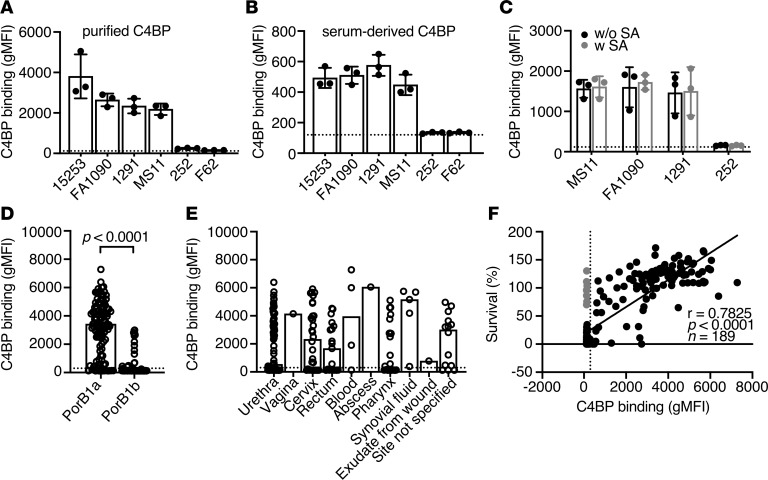
Figure 1. C4BP binds to N. gonorrhoeae.
(A and B) Binding of C4BP from normal human serum (NHS; 10%) or purified Alexa Fluor 647–labeled C4BP (20 μg/mL) to 6 laboratory strains of N. gonorrhoeae. (C) Binding of Alexa Fluor 647–labeled C4BP to 4 laboratory strains of N. gonorrhoeae in the presence (with SA) or in the absence (without SA) of sialylation. (D and E) Binding of Alexa Fluor 647–labeled C4BP (20 μg/mL) to 190 clinical isolates of N. gonorrhoeae. The isolates are grouped according to their expressed subclass of PorB and anatomical site of isolation. In D, P value was calculated by Mann-Whitney U test (P < 0.0001). (F) Spearman’s correlation analysis of survival of gonococcal clinical isolates in 10% NHS versus their C4BP binding (r = 0.7825; P < 0.0001; n = 189). Serum-resistant isolates incapable of binding C4BP are highlighted in gray. In A, B, and C bars display mean ± SD, with circles indicating independent repeats. Dotted line refers to gMFI average value in the absence of protein. In D, E, and F dotted line refers to the cutoff for positivity (300 gMFI) calculated as gMFI mean value + 3 SD of unspecific background of signal obtained for strain 252 that does not bind C4BP; bars display median and circles correspond to the mean for each sample from 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate.