Fig. 3. Structure-guided rational design and experimental validation for the conversion of sdAb JN241 antagonist into agonist.
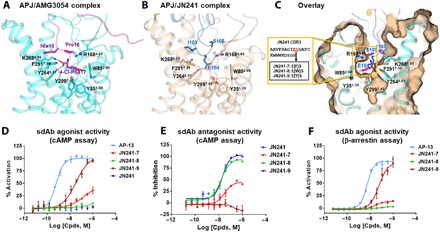
(A and B) Binding mode of peptide agonist AMG3054 in APJ-AMG3054 cocrystal structure (A) in comparison to that of JN241 CDR3 in APJ-JN241 cocrystal structure (B) at the orthostric site. AMG3054-bound APJ and AMG3054 are colored in cyan and magenta, respectively. JN241-bound APJ and JN241 are colored in light orange and sky blue, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. Key residues in the C-terminal AMG3054 (Nle15, Pro16, and 4-Cl-Phe17) and in JN241 CDR3 (I103, E104, and S105) contributing to the polar interactions and hydrophobic interactions in APJ orthosteric site are shown in sticks. (C) Surface overlay of the orthosteric site in APJ-JN241 and APJ-AMG3054 complex crystal structures. Three JN241 mutants, JN241-7, JN241-8, and JN241-9 with F, W, and Y insertion, respectively, between E104 and S105 in CDR3 were shown in the embedded box. (D and E) Functional test of JN241-7, JN241-8, and JN241-9 in the absence (D) or presence (E) of Apelin 13 (AP-13) by cAMP assay in comparison to parental sdAb JN241. (F) Functional test of JN241-7, JN241-8, and JN241-9 for agonistic activities by β-arrestin assay in comparison to AP-13. The function assays were repeated three times, and representative data are shown.
