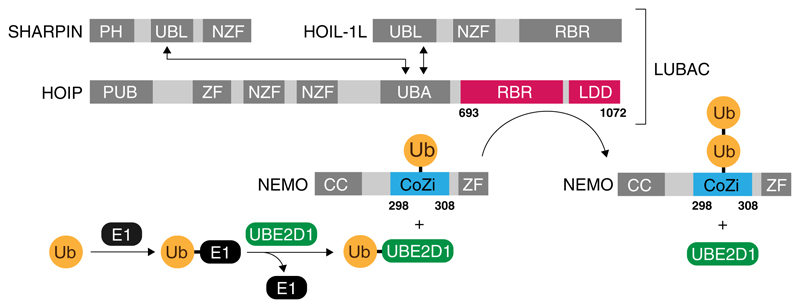
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of the ubiquitylation pathway of NEMO. Ubiquitin is activated by an E1 enzyme (black) and passed onto the E2 enzyme UBE2D1 (green) in a transthiolation reaction. LUBAC, which consists of the three proteins HOIP, HOIL-1L and SHARPIN catalyses the formation of a peptide bond between the N-terminus of a ubiquitin molecule which has been conjugated to NEMO and the C-terminus of the activated ubiquitin provided by UBE2D1. Interaction between the UBL (ubiquitin like) domains of HOIL-1L and SHARPIN with the UBA (ubiquitin associated) domain of HOIP is required for full activity under in vivo condition. The formation of di-ubiquitin conjugated to lysine 303 was reconstituted under in vitro conditions using the minimal catalytic core of LUBAC, consisting of the RBR (RING in between RING) and LDD (linear chain determining) domain of HOIP (residues 693–1072, shown red) and the fully synthetic CoZi domain of NEMO (residues 298–308, shown in blue) ligated to ubiquitin (orange). The domains of HOIP and the two proteins HOIL-1L and SHARPIN, which are not present in the reconstitution system are shaded in grey (PH peckstrin homology, NZF Npl4 zinc finger, PUB PNGase/UBA/UBX, ZF zinc finger)