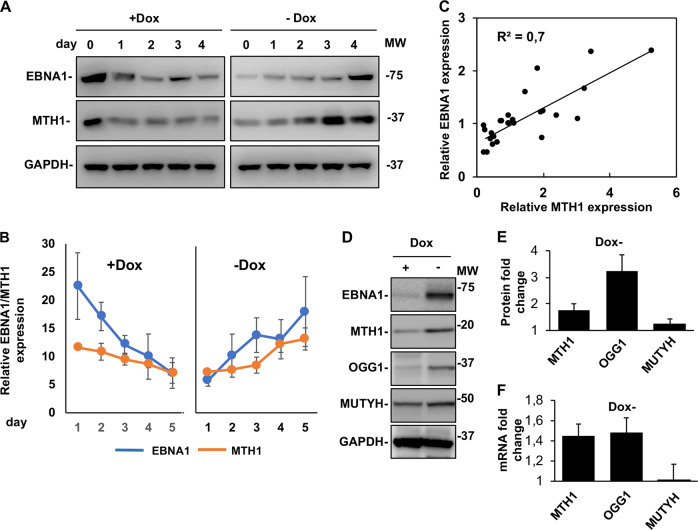
Fig. 3.
EBNA1 expression is associated with upregulation of MTH1 and oxidative damage repair pathways. The expression of MTH1, OGG1, and MUTYH was investigated by western blots and qPCR in BJAB-tTAE1 cells upon addition and withdrawal of doxycycline. a Representative western blots illustrating the correlation between the reversible down- and upregulation of MTH1 and EBNA1 in BJAB-tTAE1 cells upon addition and withdrawal of doxycycline. GAPDH was used as loading control. b Densitometry quantification of MTH1 and EBNA1 expression in BJAB-tTAE1 cells. The mean intensity of the MTH1 and EBNA1 specific bands relative to GAPDH in three independent experiments is shown in the figure. c Regression analysis of the relationship between expression levels of MTH1 and EBNA1. The data from three independent experiments were used for the plot. d Representative western blots illustrating the expression of MTH1, MUTYH, and OGG1 in BJAB-tTAE1 cells cultured for two weeks in the presence or absence of doxycycline. e Fold change is the ratio between the intensity of the specific band in cells cultured without or with doxycycline. The mean ± SD of four independent experiments is shown. f qPCR analysis of the levels of MTH1, OGG1, and MUTYH transcripts in BJAB-tTAE1 cells cultured for 2 weeks in the presence or absence of doxycycline. The mean ± SE of the fold change in six independent experiments each performed in triplicate is shown