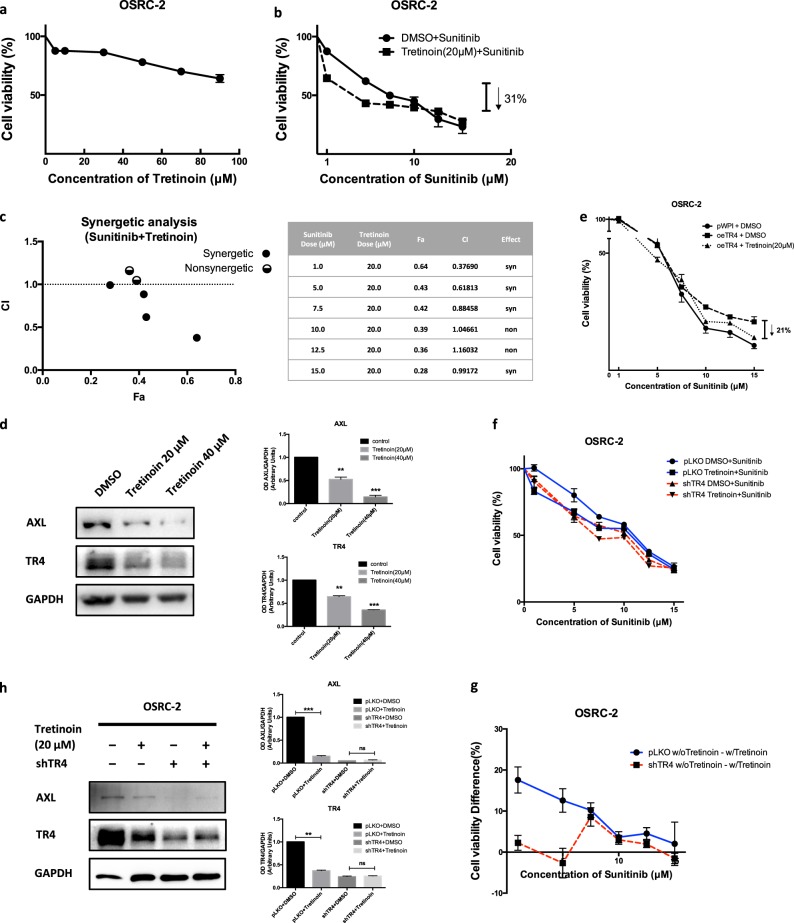
Fig. 6.
Targeting TR4/lncTASR/AXL signaling with tretinoin can increase sunitinib sensitivity to better suppress the RCC progression. a Tretinoin alone was not toxic to RCC cells. b Tretinoin can enhance the sensitivity of RCC to sunitinib when combined with low dose sunitinib. c Tretinoin actually has synergetic effects when combined with sunitinib in the treatment of RCC cells. d Western blotting (left) with quantification (right) shows that the expression of both TR4 and AXL decreased after treated with tretinoin. e Tretinoin can reverse the resistance of RCC cells to sunitinib caused by overexpressed TR4. f Viability of OSRC-2 cells in sunitinib with/without tretinoin and with/without TR4-shRNA. g DID (difference in difference) analysis shows that TR4-knockdown OSRC-2 cells have less difference change in sunitinib resistance with/without tretinoin compared with OSRC-2 cells without TR4-knockdown. h Tretinoin decreases both TR4 and AXL protein expressions in OSRC-2 cells with pLKO vehicle, but does not decrease TR4 and AXL expressions in TR4-knockdown OSRC-2 cells. Data is presented as Mean ± s.e.m., **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns not significant