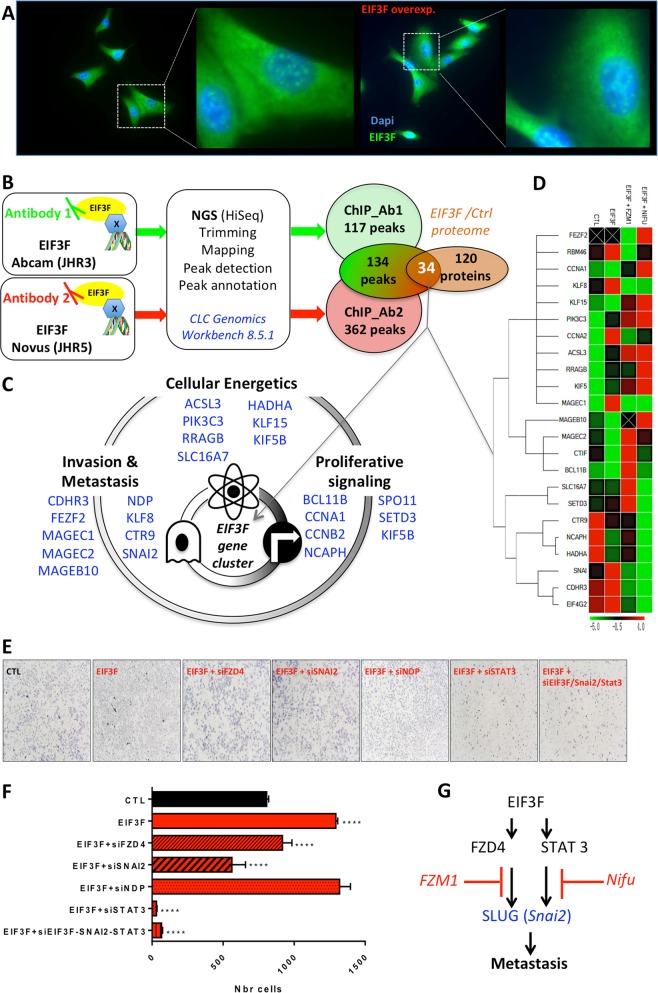
Fig. 4.
Identification of the ‘EIF3F gene cluster’. a Representative images of nuclear immuno-staining of EIF3F in CTL-A549 cells and EIF3F-A549 cells. b EIF3F gene cluster identification methods using ChIP-seq and proteomics. Following chromatin immuno-precipitation using two different antibodies, the DNA fragments associated to EIF3F were sequenced and analyzed for peak annotation. The peaks common to the two sets of experiments (134 reads) were compared to the group of proteins altered at the proteomic level (see Fig. 3) to identify the ‘EIF3F gene cluster’ composed of 34 genes. c Components of the EIF3F gene cluster were organized according to the Hallmarks of cancer based on their cellular function. d The expression of the EIF3F gene cluster components was analyzed by qPCR in A549 cells, EIF3F-A549 cells, and in A549-EIF3F cells treated with FZM1 (Frizzled-4 dependent β-catenin pathway inhibitor) and Nifuroxazide (STAT3 inhibitor) (N = 3). e Representative images, and f quantification of cell migration (transwell) assay performed in CTL-A549 cells and EIF3F-A549 cells using FZD4, SNAI2, NDP, and STAT3 siRNAs (N = 3). g Summary of the findings showing the implication of the EIF3F-FZD4-STAT3 signaling pathway in Snai2 expression and metastasis gene regulation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001