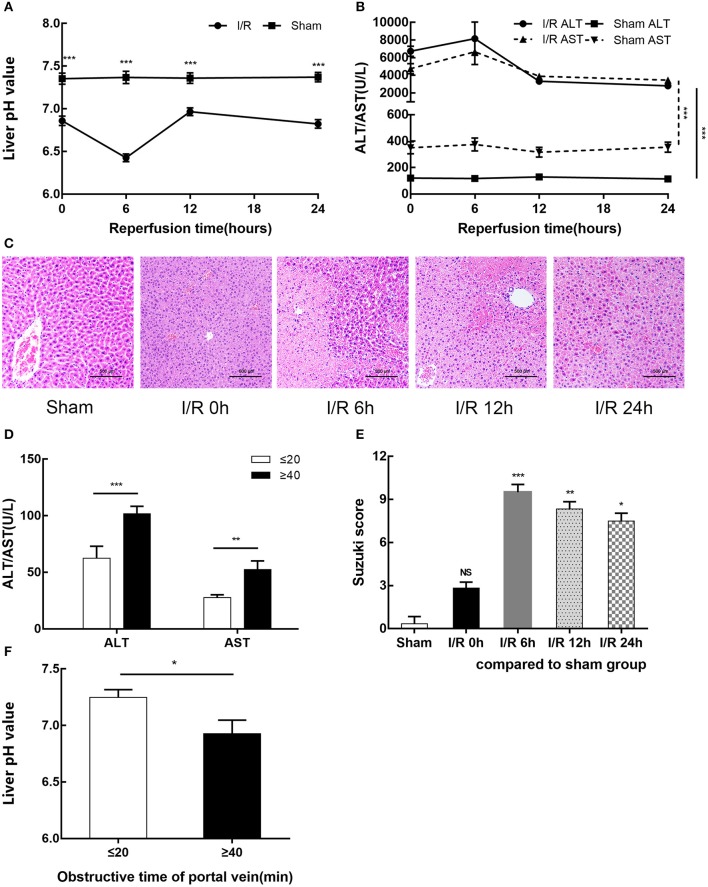
Figure 1.
HIRI causes microenvironment acidification and dysfunction of the liver in humans and mice. (A) pH value of injured liver lobe by time point after reperfusion in mice. (B) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels in sham and I/R mouse groups. (C) Representative images of mouse liver injury [hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, 200×] by light microscopy. (D) Serum ALT and AST levels of 20 patients undergoing partial hepatectomy surgery by hepatic portal occlusion time after operation. (E) Suzuki scores evaluating liver biopsies by group, as performed by an experienced pathologist. (F) pH value of excised liver tissue of 20 patients undergoing partial hepatectomy surgery by hepatic portal occlusion time. Data are presented as the means ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.