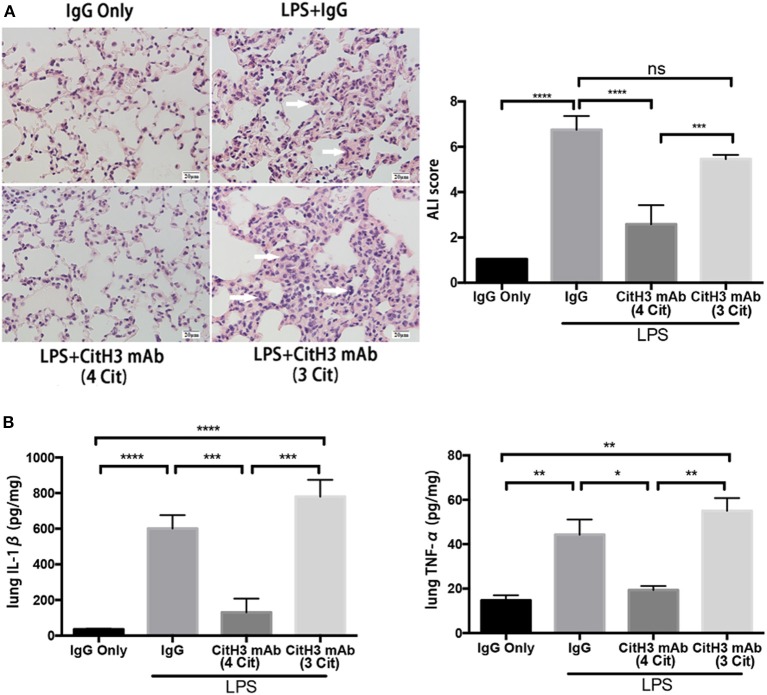
Figure 4.
The CitH3 mAb (4 Cit) ameliorates acute lung injury in lethal endotoxic shock. Mice were randomly divided into four groups: (1) IgG only (20 mg/kg), (2) LPS (20 mg/kg) + IgG (20 mg/kg), (3) LPS + CitH3 mAb (4 Cit) (20 mg/kg), and (4) LPS + CitH3 mAb (3 Cit) (20 mg/kg) (n = 3/group). Blood and organs were harvested at 12 h after LPS injection. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse lung sections is shown, and histological analysis of acute lung injury (ALI) was graded by a blinded pathologist and presented as ALI score (mean ± SEM, n = 3/group). White arrows indicate inflammatory changes. (B) IL-1β and TNF-α of lung homogenates were determined by ELISA. Cytokine levels were normalized by protein concentration and were significantly lower in CitH3 mAb (4 Cit)-treated mice (mean ± SEM, n = 3/group). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. ns, non significance.