Figure 7.
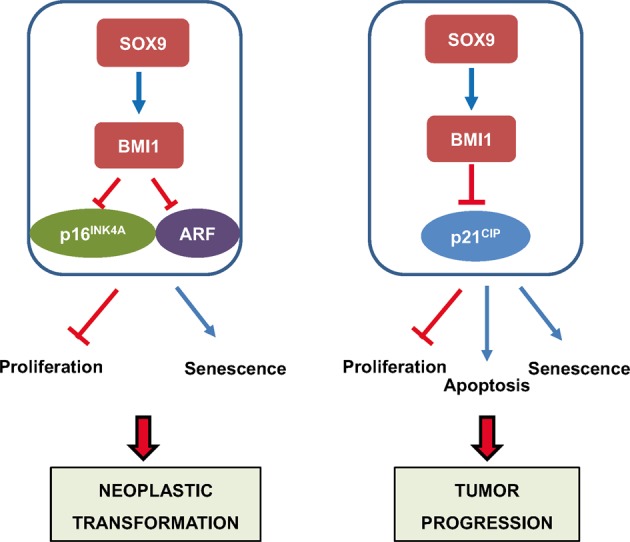
Pro-tumoral action and molecular mechanism of SOX9 in cancer. In the context of non-tumor cells (left panel), SOX9 is able to promote neoplastic transformation through the induction of cell proliferation and the evasion of senescence. At the molecular level, this transformation takes place through the induction of BMI1 expression, which represses the expression of the tumor suppressors p16INK4A and ARF (previously described by Matheu et al., 2012). In the context of tumor cells (right panel), generally deficient in p16INK4A and ARF expression, SOX9 enhances tumor progression through the promotion of cell proliferation and the evasion of apoptosis and senescence. In this context, the molecular mechanism involves the repression of the tumor suppressor p21CIP.
