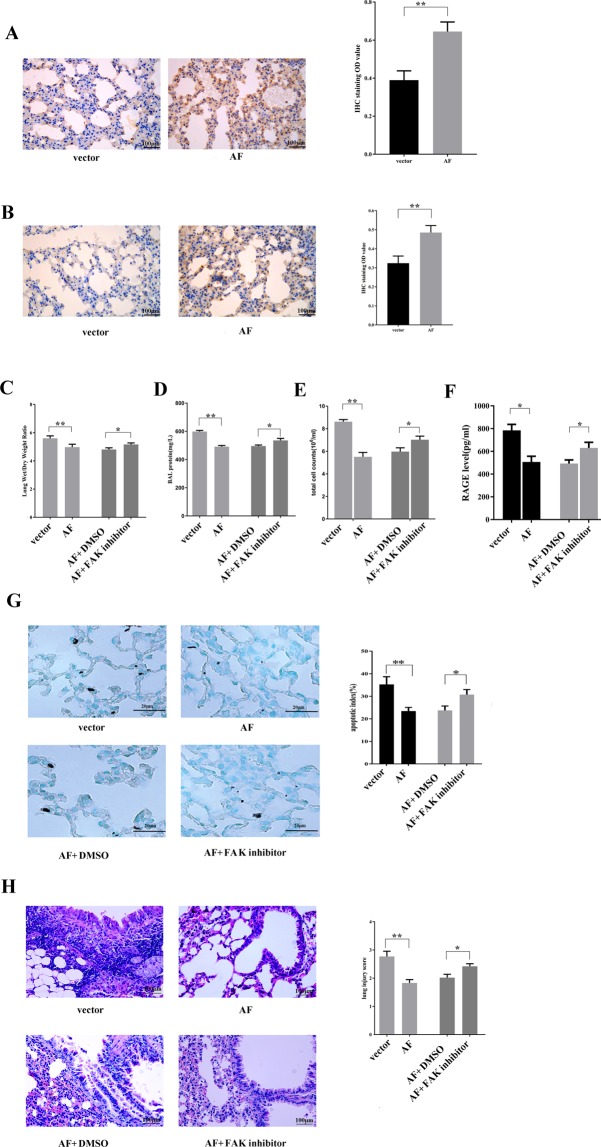
Figure 5.
FAK supplementation decreases lung injury in mice challenged with 4 h of HMV. Representative images (IHC staining, 400×) and the relative semiquantitative analysis showing that FAK recombinant adenovirus (AF) injection enhanced the expression of FAK (A) and phospho-Akt (B) in AECs. The lung wet/dry ratio (C), BALF protein level (D), BALF cell counts (E) and RAGE level in the BALF (F) in the different groups of mice are shown. (G) Representative images (400×) of apoptosis in AECs, as visualised by TUNEL staining, and the quantification of the results. (H) Representative images (H&E, 400×) of lung tissue and the quantification of lung injury. FAK supplementation attenuated injury, inducing a decreased lung injury score and apoptosis index in lung tissues, as well as a lower protein level, RAGE level and cell counts in the BALF, whereas the protective effect of FAK was blocked by a FAK inhibitor. Lung injury was triggered by HMV, and mice received different treatments before HMV as follows: injection with vector only (vector); FAK recombinant adenovirus injection (AF), AF plus FAK inhibitor or DMSO. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 by two-tailed t test).