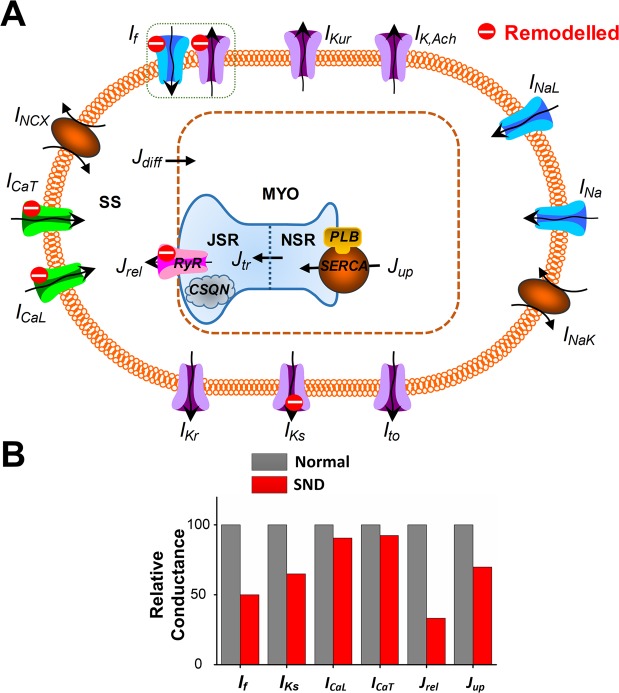
Figure 1.
Illustration of atrial fibrillation (AF)-induced remodelling processes and electrophysiological properties and calcium dynamics in the human sinoatrial node (SAN) cell model. (A) Schematic presentation of the cell model. Formulations for AF-induced remodelled currents and fluxes (red) were based directly on experimental data of the canine model of pacing-induced AF. The model includes four compartments: bulk myoplasm (myo), junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (JSR), network sarcoplasmic reticulum (NSR), and subspace (SS). Currents into the subspace: funny current (If; representing both sodium and potassium components), L-type calcium current (ICaL), T-type calcium current (ICaT), fast sodium current (INa), transient outward potassium current (Ito), rapid delayed rectifier potassium current (IKr), slow delayed rectifier potassium current (IKs), ultrarapid delayed rectifier potassium current (IKur), acetylcholine-sensitive muscarinic potassium current (IKACh), sodium-calcium exchange current (INCX) and sodium-potassium pump current (INaK). Ionic fluxes: calcium flux (Jrel) through ryanodine receptor (RyR), NSR to JSR calcium translocation (Jtr), calcium uptake (Jup) into NSR via SERCA/phospholamban (PLB) and diffusion calcium flux from subspace to myoplasm (Jdiff). AF-induced targets: If, ICaT, ICaL, Jrel R and Jup. (B) Relative conductance between normal and SND conditions.