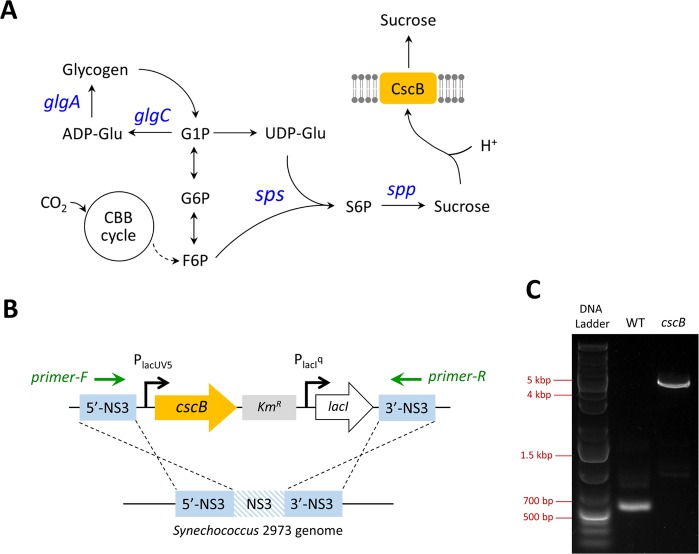
Figure 1.
Engineering of Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 for production of sucrose. (A) Metabolic pathways of carbohydrate biosynthesis in Synechococcus 2973. The sucrose permease CscB was expressed for sucrose excretion. Genes highlighted in blue encode enzymes for glycogen and sucrose production. In Synechococcus 2973, the SPS enzyme has both sucrose-phosphate synthase and sucrose-phosphate phosphatase activities. (B) Introduction of the cscB gene into the neutral site 3 (NS3). The primers used for PCR genotyping are highlighted in green. (C) PCR genotyping to confirm complete segregation of cscB. The wild type (WT) Synechococcus 2973 was used as a control. The PCR product of the WT gene is 514 base pairs (bp). No WT copy was present in the cscB-expressing strain. ADP-Glu, adenosine diphosphate glucose; CBB cycle, Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle; CscB, sucrose permease; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; G1P, glucose 1-phosphate; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; S6P, sucrose 6-phosphate; UDP-Glu, uridine diphosphate glucose; glgA, glycogen synthase; glgC, ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; spp, sucrose-phosphate phosphatase; sps, sucrose-phosphate synthase.