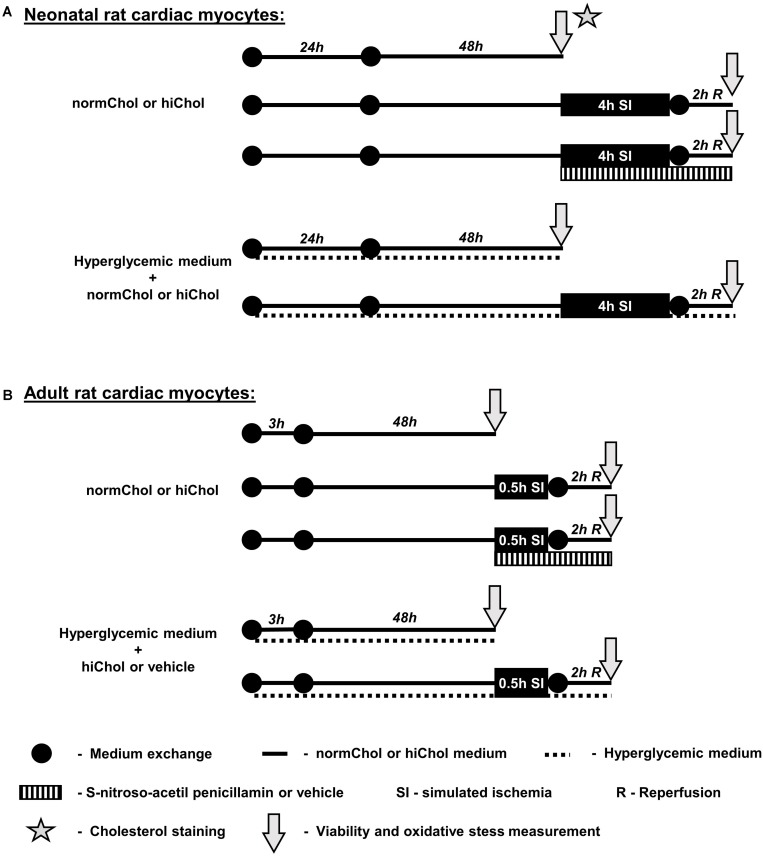
FIGURE 1.
(A) Neonatal cardiomyocytes were cultured in normo glycemic or hyperglycemic medium supplemented with vehicle or hypercholesterolemic supplementation (hiChol). Cholesterol staining was to show the effect of hiChol supplementation. Cell viability and oxidative stress, i.e., total reactive oxygen species (ROS) and superoxide level was measured by fluorescent assays after 72 h cultivation. Each group was subjected to normoxia or simulated ischemia/reperfusion injury (SI/R), respectively. Viability and oxidative stress was measured after normoxia or SI/R. (B) In adult rat cardiomyocytes treated with vehicle or hiChol supplements cell viability and oxidative stress was measured under normoxia or after SI/R injury.