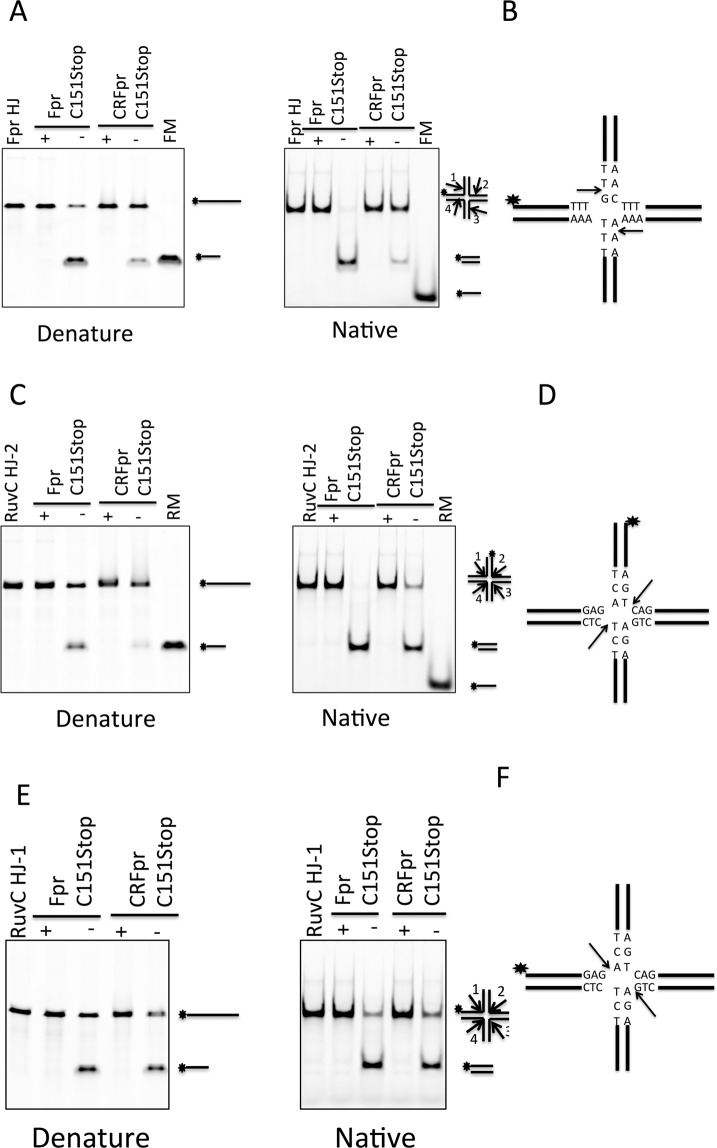
Figure 6.
Comparison of the HJ cleavage activities of Fpr C151stop and CRFpr C151 stop. (A) Cleavage of FprHJ substrate by Fpr and CRFpr. The reaction mixture (20 μl) containing Fpr dimer (300 nM) or CRFpr dimer (300 nM) with FprHJ (100 nM), was incubated at 37 °C for 10 min. The reaction products were separately analyzed on denaturing (left) and native gels (right). FprHJ, FprHJ alone in reaction buffer as a control. FM, FprHJ marker. (B) Central sequences of FprHJ. The star indicates the fluorescently labeled position and arrows indicate the cleavage positions. (C) Cleavage of the bimobile RuvCHJ-2 substrate by Fpr and CRFpr. The reaction condition was the same as above. RuvCHJ-2 has 6-FAM label at the 5′ of strand 2. RM, RuvCHJ marker. (D) Central sequences of RuvCHJ-2. The star shows the labeled position and arrows indicate the cleavage positions. (E) Cleavage of RuvCHJ-1 substrate by Fpr and CRFpr. The reaction condition was the same as above. RuvCHJ-1 has 6-FAM label at the 5′ of strand 1. RM, RuvCHJ marker. (F) Central sequences of RuvCHJ-1. The star shows the labeled position and arrows indicate the cleavage positions. Each DNA cleavage experiment was repeated 3 times and a representative gel is shown in the figure. Original full-length gels for Fig. 6 are shown in Supplementary Figure S12.