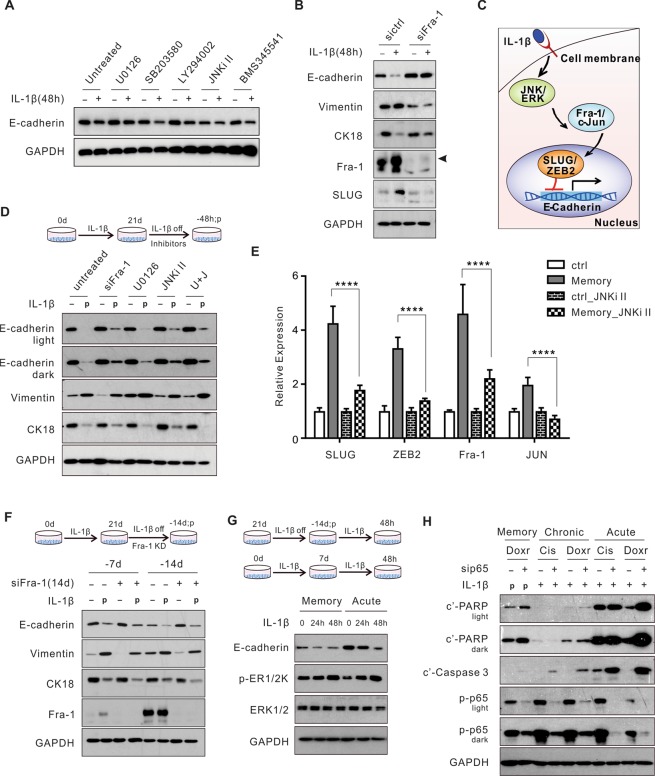
Figure 4.
Pathways mediating acute EMT are not required for the maintenance of chronic EMT or EMT memory. (A) E-cadherin expression following 48 hours of chemical inhibition of IL-1β-activated signaling pathways. (B) A549 cells were exposed to IL-1β for 48 hours following Fra-1 knockdown and examined for EMT markers. (C) A schematic mechanism of the IL-1β-induced acute EMT in A549 cells. (D) Evaluation of EMT markers with 48-hour inhibition of the MAPK (ERK and JNK) - AP-1 - SLUG axis in EMT memory. (E) Expression of SLUG, ZEB2, Fra-1, and JUN upon the JNK inhibition in EMT memory (-7d). (F) Expression of EMT markers with 14 days of Fra-1 knockdown (KD) following IL-1β withdrawal from the chronic treatment. (G) E-cadherin level and ERK signaling activity in A549 cells when being re-exposed to IL-1β after either 14 days of IL-1β withdrawal in EMT memory or 7 days of IL-1β exposure in acute EMT. (H) Evaluation of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis upon p65 knockdown in acute (48 hours), chronic EMT (24 days), and EMT memory (-7 days). U0126, ERK pathway inhibitor; SB203580, p38 inhibitor; LY294002, PI3K inhibitor; JNKi II, JNK inhibitor; BMS345541, IKK inhibitor; “U + J”, U0126 and JNKi II combination treatment. “-d/-h”, days/hours after IL-1β withdrawal; “p”, previously treated with IL-1β. Cis, cisplatin; Doxr, doxorubicin. All results are reported as mean ± SEM. ****P < 0.0001. See also Fig. S4.