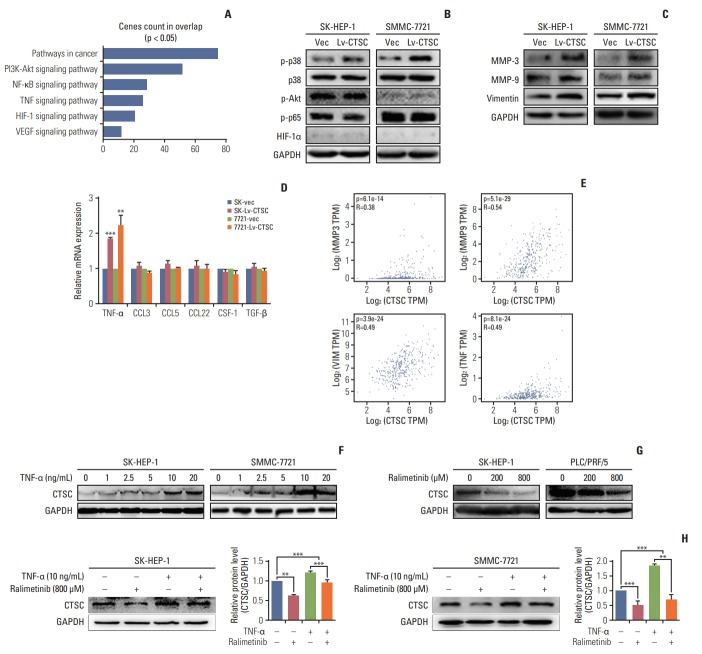
Fig. 4.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK, p38) pathway is involved in cathepsin C (CTSC) mediated hepatocellular carcinoma progression. (A) The signaling pathway acquired by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. (B) The activation of TNF-α/MAPK (p38) signaling pathway after overexpressing CTSC in SK-HEP-1 and SMMC-7721 cells, demonstrated by western blot assay. (C) The expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 3, MMP-9, vimentin after CTSC overexpression in SK-HEP-1 and SMMC-7721 cells detected by western blot assay. (D) The expression of TNF-α after overexpressing CTSC in SK-HEP-1 and SMMC-7721 cells detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (E) The correlation between CTSC and MMP-3, MMP-9, Vimentin, and TNF-α in clinical specimens analyzed by the GEPIA. (F) The western blot assay was used to investigate the effect of TNF-α on CTSC expression. (G, H) The western blot assay was used to investigate the effect of Ralimetinib on CTSC expression. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.