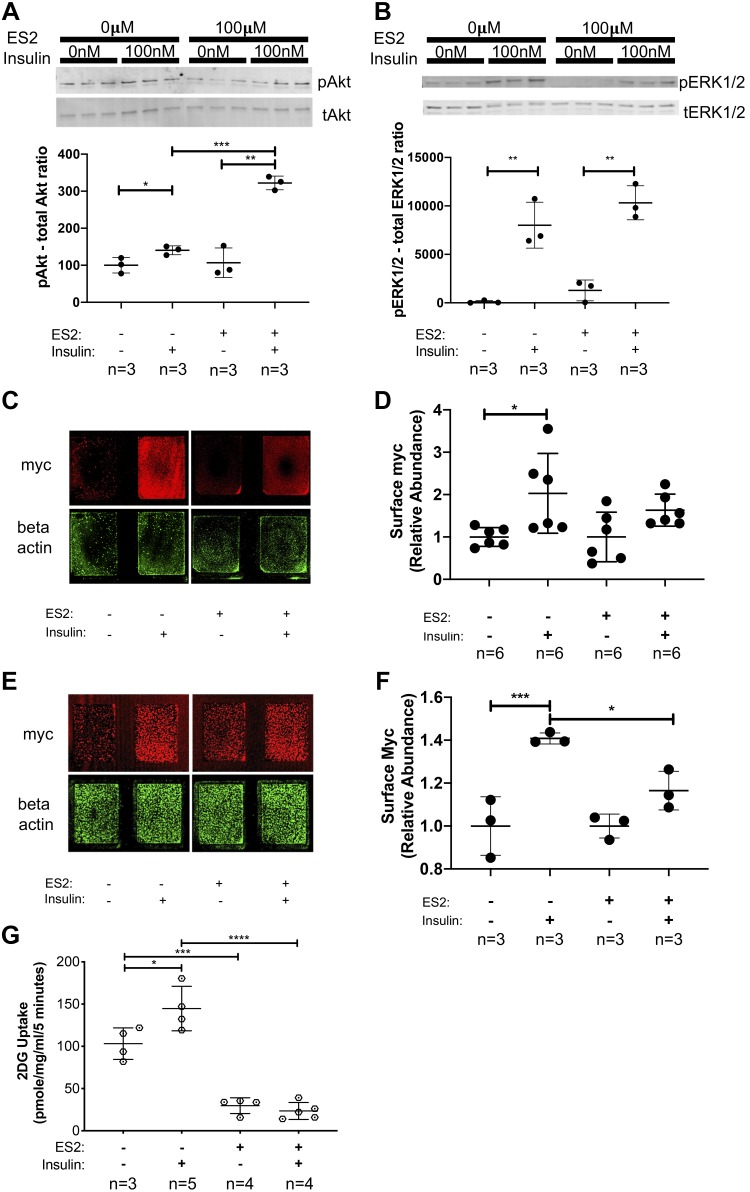
Fig. 5.
Endosidin 2 (ES2) treatment hinders insulin-induced cell surface delivery of GLUT4myc and subsequent glucose uptake. A and B: analysis of insulin signaling pathway activation in the presence of exocyst inhibitor ES2. Phosphoprotein levels of both pAkt and pERK1/2 targets were normalized to total protein levels of Akt and Erk1/2, respectively. Data, representative of 3 independent experiments, are presented as means ± SD in relative units; n, no. of replicates. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.005. C: representative immunofluorescent staining of cell surface GLUT4myc in L6 GLUT4myc myoblasts treated with insulin in the presence or absence of ES2. Signal intensities of entire surface of the chamberslide wells were measured with a fluorescent scanner, and surface GLUT4myc levels were normalized to β-actin levels measured after a subsequent permeabilization and immunostaining of the samples. D: quantification of relative cell surface GLUT4myc levels in myoblasts treated with insulin in the presence or absence of ES2. Data are means ± SD in arbitrary units relative to untreated control; n, no. of replicates. *P < 0.05. E: representative staining of cell surface GLUT4myc in differentiated L6 GLUT4myc myotubes treated with insulin in the presence or absence of ES2. Signal intensities of surface GLUT4myc were normalized to β-actin levels as described above. F: quantification of relative cell surface GLUT4myc levels in differentiated myotubes treated with insulin in the presence or absence of ES2. Data are means ± SD in arbitrary units relative to untreated control; n, no. of replicates. *P < 0.05. ***P < 0.005. G: measurement of 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2DG) uptake in skeletal myoblasts in response to insulin in the presence or absence of ES2. Data are means ± SD; n, no. of replicates. *P < 0.05. ***P < 0.005. ****P < 0.001. Images and data presented are representative of 3 independent preparations.