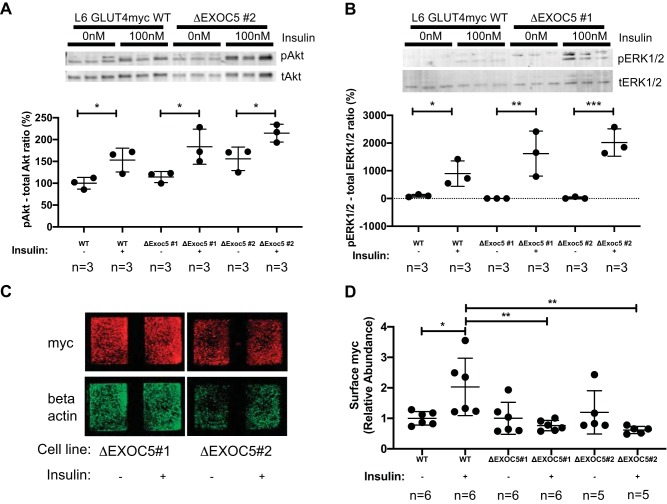
Fig. 7.
Heterozygous knockout of EXOC5 results in decreased cell surface delivery of GLUT4myc in response to insulin. A and B: analysis of insulin signaling pathway activation in ΔExoc5 clones in response to insulin-representative Western blots and quantification. Levels of both pAkt and pERK1/2 targets were normalized to total protein levels of Akt and Erk1/2, respectively. C: representative immunofluorescent staining of cell surface GLUT4myc in ΔExoc5 L6 GLUT4myc myoblasts treated with insulin. Signal intensities of surface GLUT4myc detected by an anti-myc antibody were normalized to β-actin levels measured after a subsequent permeabilization and immunostaining of the samples. D: quantification of relative cell surface GLUT4myc levels in wild-type (WT) and ΔExoc5 L6 GLUT4myc myoblasts treated with insulin. Images and data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Values are means ± SD in relative units (vs. WT L6-GLUT4myc cells); n, no. of replicates. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.005.