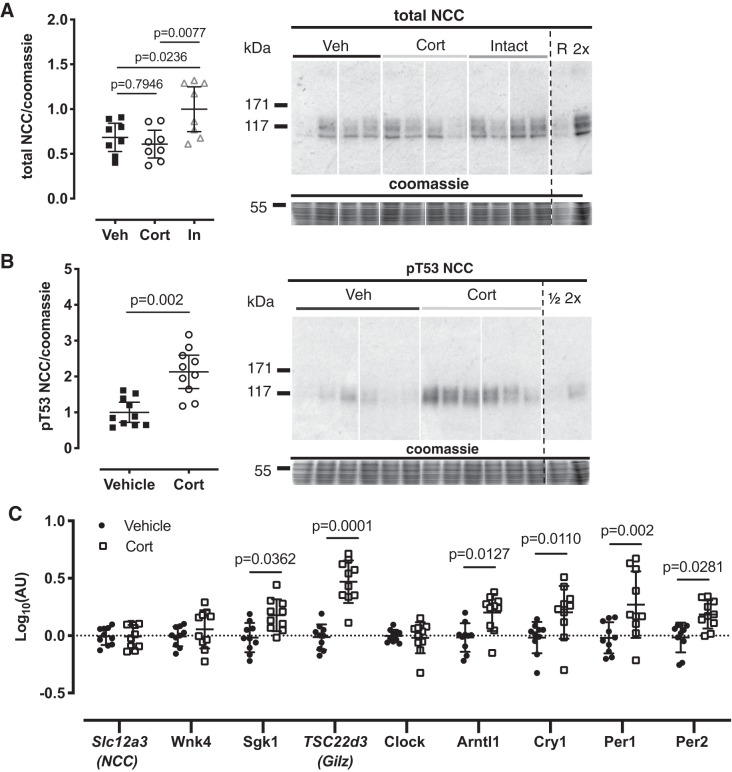
Fig. 1.
Adrenalectomy reduces total levels of the sodium-chloride cotransporter (NCC, A). In adrenalectomized animals, acute corticosterone injection induced an upregulation of NCC phosphorylation at Thr53 (B), accompanied by changes in gene expression (C). C57BL6 mice were adrenalectomized [vehicle (Veh)/corticosterone (Cort)] or undisturbed (In), and all were maintained on 0.9% saline in place of drinking water. Mice then received an acute intraperitoneal injection of vehicle (Veh/Intact) or corticosterone, and kidneys were taken 6 h later for Western blot analysis. All samples were run on the same blots or evenly distributed across blots and normalized to a reference lane. All rearrangements of blots are for clarity. Signal densities for immunoblots were normalized to Coomassie signal densities and to the reference lane (R) and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc Tukey’s tests (n = 8 biological replicates, A), t-tests (n = 10, B), or two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Sidak’s tests (n = 10, C). Data are means ± SD. See Table 1 for gene descriptions and protein names.