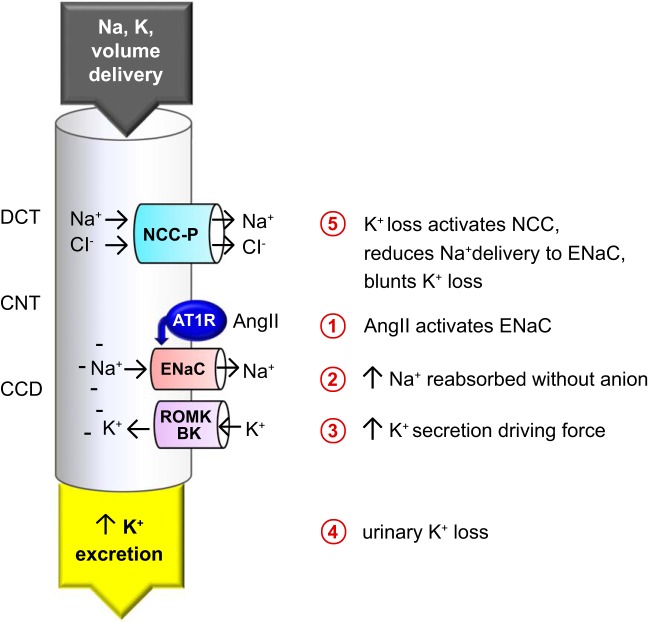
Fig. 7.
Schematic representation of the impact of angiotensin II (ANG II) on Na+ and K+ transport in the distal nephron. The proposed chain of events is illustrated, connecting direct ANG II activation of epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) (1) with indirect activation of Na+-Cl− cotransporter (NCC) phosphorylation mediated by coupling of Na+ reabsorption (2) with K+ secretion (3) in the connecting tubule (CNT) and cortical collecting duct (CCD) driving urinary K+ loss (4), which activates NCC via phosphorylation (NCC-P) (5) to minimize Na+ delivery to ENaC to blunt further K+ loss. AT1R, ANG II type 1 receptor; BK, large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel; DCT, distal convoluted tubule; ROMK, renal outer medullary K+ channel.