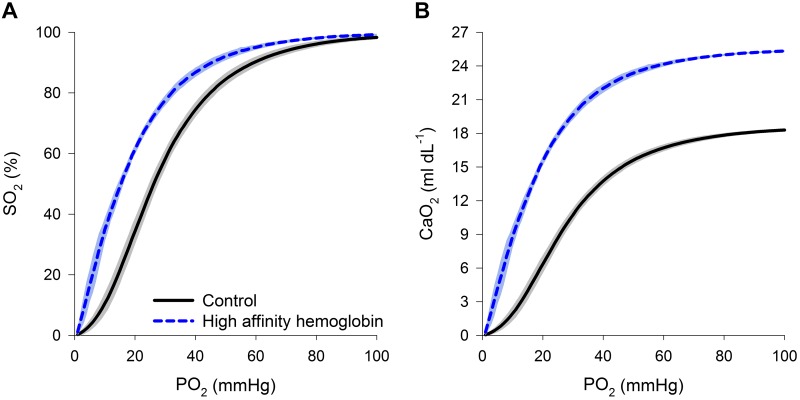
Fig. 2.
A and B: composite oxyhemoglobin dissociation curves (A) and arterial oxygen content curves (B) for the control subjects and those with high-affinity hemoglobin. Arterial oxygen content was calculated with corresponding oxyhemoglobin dissociation curves and resting hemoglobin concentration. The line represents the mean, and the shaded area represents 1 SD. So2, oxyhemoglobin saturation; Po2, oxygen tension; , arterial oxygen content.