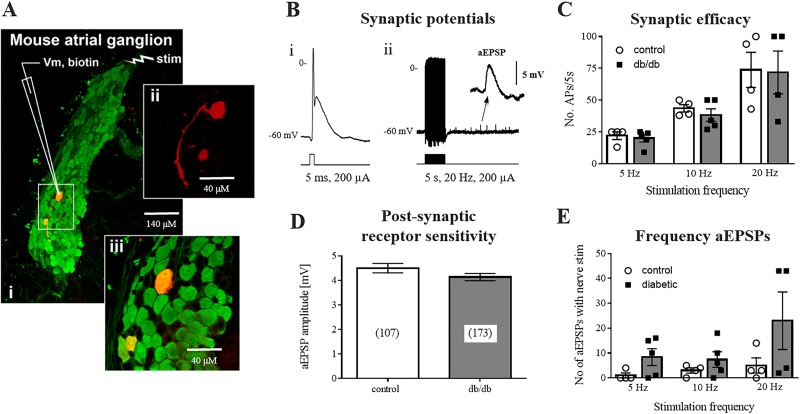
Fig. 2.
Preserved synaptic transmission at intrinsic cardiac neurons (ICNs). A: intracellular membrane potential was recorded from individual ICNs impaled with glass microelectrodes in isolated preparations of intrinsic cardiac ganglia. A single atrial ganglion (i) is shown [protein gene product 9.5 (PGP9.5), green], containing an individual neuron backfilled with Neurobiotin (red) (ii and iii). Scale bars = 140 μM (i) and 40 μM (ii and iii). B: examples of the suprathreshold postsynaptic potential recorded from a neuron during either a single (i) or train (ii) of presynaptic shocks. Note the occurrence of asynchronous excitatory postsynaptic potentials (aEPSPs; inset) following tetanic stimulation. C: synaptic efficacy, shown as the number of action potentials (APs) elicited by a train of presynaptic stimuli. D: summed amplitude of aEPSPs was not significantly different between control or db/db mice, indicating no loss of function of postganglionic nicotinic receptors. E: number of aEPSPs occurring at multiple frequencies of presynaptic stimulation were not different between control and db/db mice. Control: 12 cells from 5 animals; db/db: 17 cells from 7 animals.