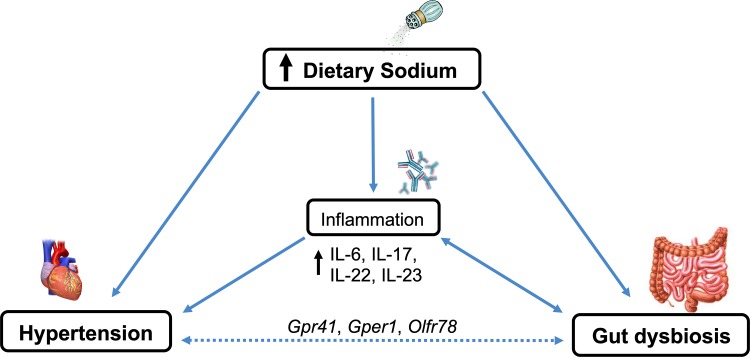
Fig. 1.
Interactions between dietary sodium, hypertension, and the gut microbiota. High dietary sodium consumption may contribute to gut dysbiosis, as it alters gut microbial composition, richness, and diversity. High dietary sodium also induces inflammation through increased production of inflammatory cytokines that can directly increase blood pressure (BP). Potential mechanism of BP increase via the gut microbiota is through G protein-coupled (Gpr) and olfactory (Olfr) receptors in the vasculature or through an inflammatory response. Gper, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor; IL, interleukin.