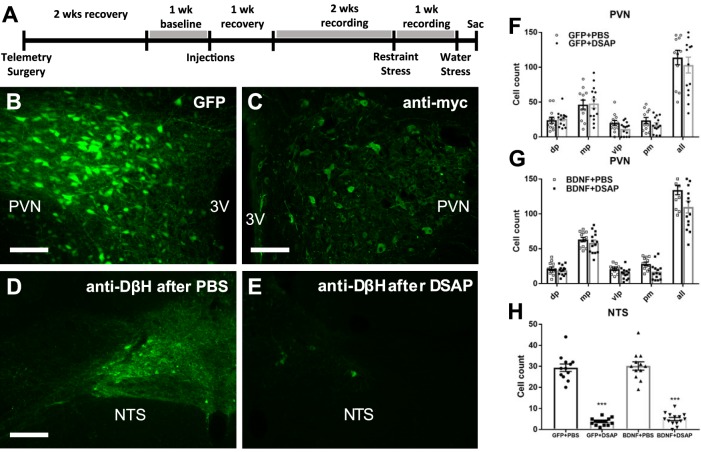
Fig. 1.
A: timeline of experiment 1. B and C: representative fluorescent images of coronal brain sections ~1.8 mm posterior from bregma showing PVN expression of GFP and BDNFmyc, respectively. BDNFmyc expression was detected with an anti-myc tag antibody and immunofluorescence; scale bars = 100 µm. D and E: representative fluorescence images showing DβH expression in the NTS in coronal brain sections at the level of the calamus scriptorius following PBS and DSAP injections, respectively; scale bars, 100 µm. F and G: number of GFP- and myc-positive cells was assessed in subnuclei of the PVN; dorsal parvocellular nuclei (dp), medial parvocellular nuclei (mp), ventrolateral parvocellular nuclei (vlp), and posterior magnocellular nuclei (pm) following AAV2-GFP or AAV2-BDNFmyc injections in the PVN and PBS or DSAP injections in the NTS. DSAP had no significant effect on vector mediated gene transduction in GFP or BDNF rats. GFP+PBS (n = 12), GFP+DSAP (n = 14), BDNF+PBS (n = 12), BDNF+DSAP (n = 14); n refers to number of PVN sides. H: number of DβH-positive neurons in the NTS following AAV2-GFP or AAV2-BDNFmyc injections in the PVN and PBS or DSAP injections in the NTS. DSAP significantly reduced the number of DβH-positive neurons in both the GFP and BDNF groups. 3V, third ventricle; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; GFP, green fluorescent protein; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BDNFmyc, myc epitope-tagged BDNF; DβH, dopamine β-hydroxylase; DSAP, anti-dopamine-β-hydroxylase-conjugated saporin; AAV2, adeno-associated viral vector 2. ***P < 0.001 for DSAP (1-way ANOVA).