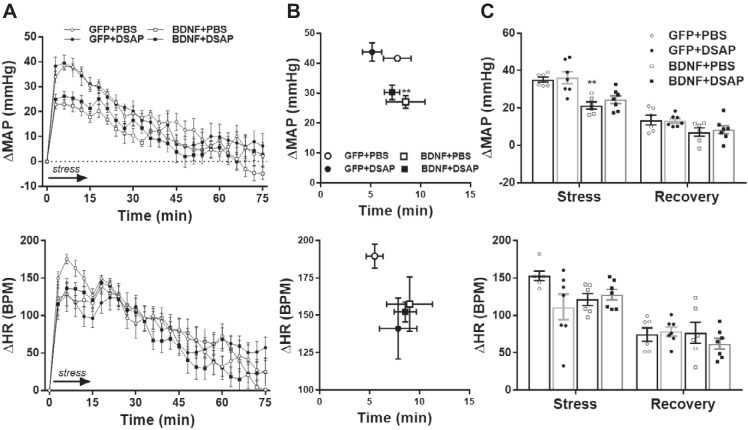
Fig. 5.
Radiotelemetric recordings of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) during acute water stress and poststress recovery in GFP+PBS (n = 6), GFP+DSAP (n = 7), BDNF+PBS (n = 6) and BDNF+DSAP (n = 7) rats. A: MAP (top) and HR (bottom) traces with 3-min moving average during stress (15 min, indicated by arrow) and during poststress recovery (60 min). B: amplitude and delay of peak MAP and HR responses. C: MAP and HR increases averaged during stress and poststress recovery. Prestress MAP and HR were 94 ± 3 mmHg and 308 ± 11 beats/min (bpm) in the GFP+PBS group, 101 ± 4 mmHg and 327 ± 9 beats/min in the GFP+DSAP group, 121 ± 4 mmHg and 366 ± 19 beats/min in the BDNF+PBS group, and 113 ± 5 mmHg and 378 ± 11 beats/min in the BDNF+DSAP group. GFP, green fluorescent protein; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; DSAP, anti-dopamine-β-hydroxylase-conjugated saporin. Results represent means ± SE. **P < 0.01 for GFP+PBS vs. BDNF+PBS (1-way ANOVA).