Figure 1.
Apancreatic Phenotype of the PDX1−/− Fetus and Restoration of Pancreatogenesis by Blastocyst Complementation
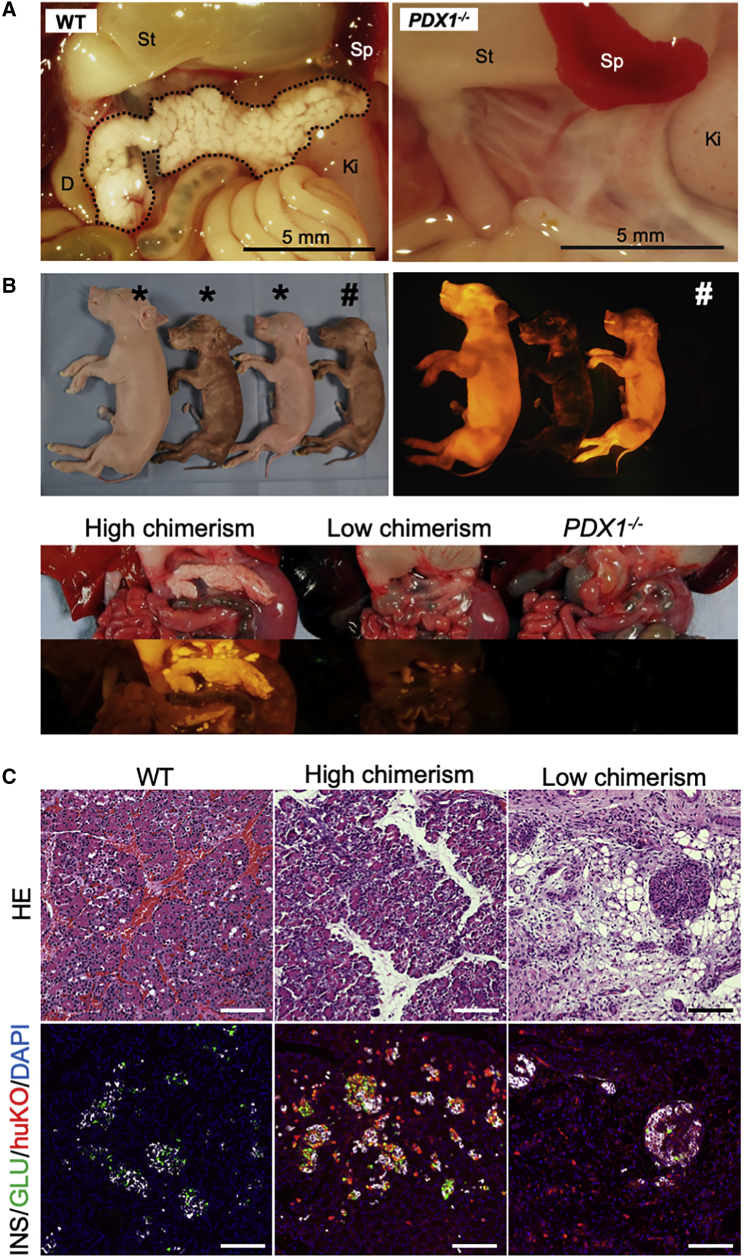
(A) Apancreatic phenotype of a PDX1−/− cloned fetus at mid-gestation (day 55; WT, day 66).
(B) Chimeric full-term fetuses (three left animals in upper panels) and restored pancreata (lower panels). Fetuses exhibiting huKO fluorescence and male phenotype were determined as chimeras. Chimeric fetuses (∗) indicating higher level of systemic chimerism showed well-restored pancreata (leftmost in lower panels), while development of pancreatic tissue was poor in a fetus with lower chimerism (center in lower panels). The rightmost animal in upper panels (#) presents a PDX1-KO fetus showing typical features of the apancreatic phenotype (lower panels).
(C) Histological features of the pancreatic tissue generated by blastocyst complementation. Upper panels: H&E-stained sections. Lower panels: sections immunostained for insulin (white), glucagon (green), and huKO (red). Restored pancreatic tissue of the fetus (center) with higher chimerism entirely expressed huKO fluorescence. Scale bars, 100 μm.