Figure 3.
Detecting Recurrent Genetic Abnormalities by Focused ddPCR
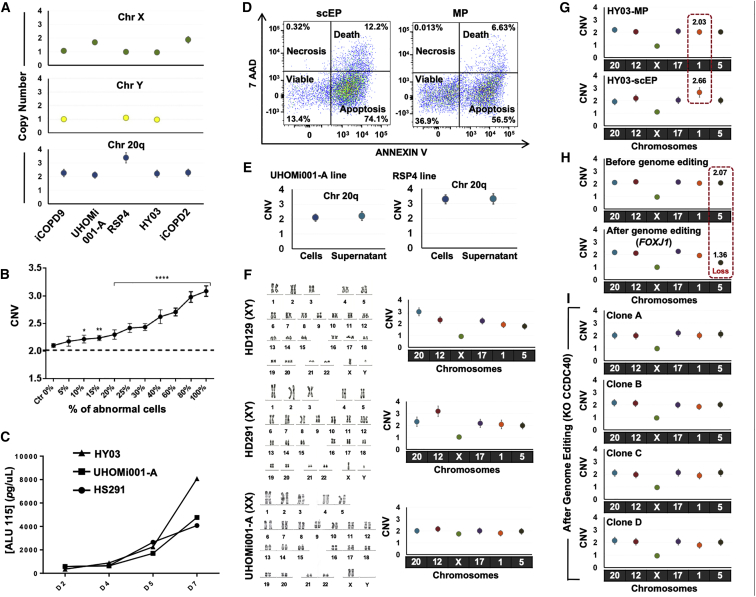
Each ddPCR data point is obtained from one sample using Poisson statistics and error bars indicate the Poisson distribution at 95% confidence intervals.
(A) Copy-number variation analysis using droplet digital PCR and DNA extracted from different hPSC lines in culture.
(B) Sensitivity of the droplet digital PCR method for detecting increasing percentages (from 0% to 100%) of hPSCs harboring a trisomy 12 within a sample of euploid hPSCs. The panels represent three independent experiments (p < 0.05, Student's t test).
(C) Quantification of DNA in supernatant samples from one hESC line (HS291) and two hiPS lines (HY03 and UHOMi001 cells) cultured in E8 medium on Geltrex matrix. Supernatant was collected at the indicated days (D) after seeding (75,000 cells/well in a 35-mm plate). DNA was extracted from 300 μL of supernatant and quantified by ALU-qPCR with ALU115 primers.
(D) The percentage of apoptotic, necrotic, and viable cells in supernatant samples collected at day 5 was evaluated by flow cytometric analysis after staining with annexin V and 7-amino-actinomycin (7-AAD). Every dot corresponds to a single cell. ScEP, single-cell enzymatic passaging; MP, mechanical passaging.
(E) Copy number of chromosome 20q measured by ddPCR using genomic DNA from cells and supernatant as template. The error bar varies in function of the DNA source (cells or supernatant).
(F) The iCS-digital test using six probes for chromosomes 20q, 12, X, 17, 1, and 5 can identify aneuploidy. The hPSC lines HD129 (chromosome 20 triploidy), HD291 (chromosome 12 triploidy), and UHOMi001-A (euploid) were analyzed by karyotyping (classical G-banding) and with the iCS-digital test using probes targeting common abnormal regions on chromosomes 20q, 12, X, 17, 1, and 5. Karyotype images are reprinted from Stem Cells Dev. 24(5):653-62, 2015 and Stem Cell Res. 33:15-19, 2018 with permission from Elsevier.
(G) Identification of genome modifications associated with culture conditions using the iCS-digital test. After 15 passages using single-cell enzymatic passaging, the HY03 hiPSC line displayed a copy-number gain on chromosome 1 (2.66), suggesting a mosaic cell population that comprises an abnormal clone with at least three genome copies at the probe location.
(H) Analysis of genome stability using the iCS-digital test in the male hiPSC line HY03 before (mechanical passage M53, clumps passage Cl2, single-cell passage SC11) and seven passages after genome editing.
(I) CNV characterization of chromosome 20q, 12, X, 17, 1, and 5 in four CCDC40_KO HY03 clones obtained using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. No abnormality was detected in any of the four clones.