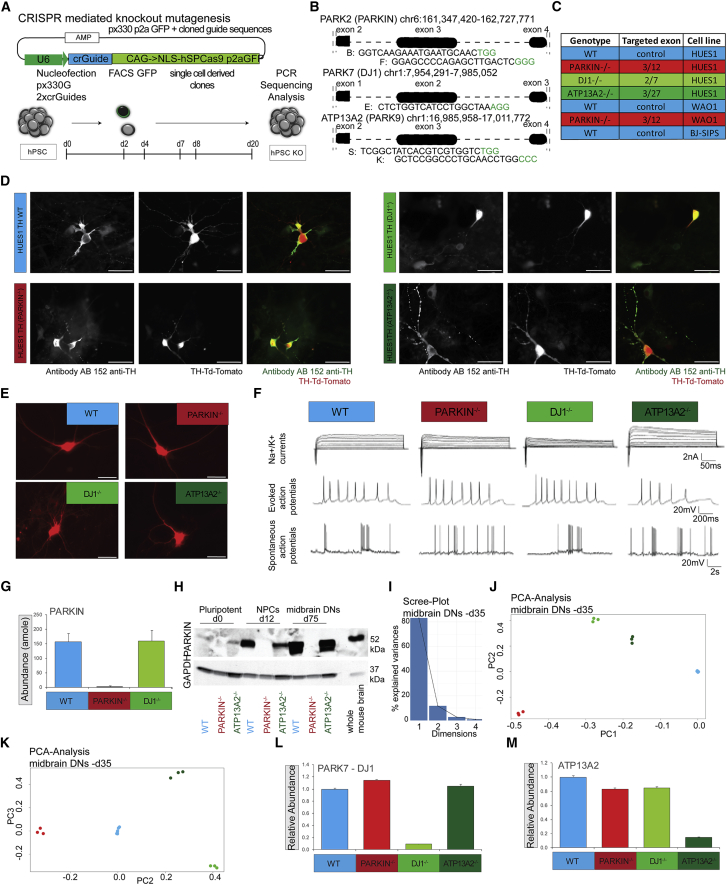
Figure 2.
Generation, and Molecular and Functional Characterization of Knockout Cell Lines in the PD Model
(A) Experimental Scheme depicting the CRISPR knockout mutagenesis strategy.
(B) Graphical display of chromosome positions, targeted exons, and CRISPR sequences.
(C) Table summarizing knockouts indicating targeted exons, and coloring scheme used in this study in isogenic HUES1, WA01 and BJ-SIPS lines: WT, PARKIN−/−, DJ-1−/−, and ATP13A2−/−.
(D) Fluorescence microscopy panel, showing HUES1-derived DNs at d35 from all isogenic reporter cell lines, dissociated on d25 and plated in low density on mouse glial cells. Scale bars, 100 μm, 40× (left, ICC stained with TH antibody AB152; middle, TH:TdTomato reporter fluorophore expression, right merge).
(E) Fluorescence microscopy images of flow sorted TH+ neurons from all isogenic lines 4 weeks post plating on glial cells before electrophysiological analysis. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(F) Whole-cell patch clamp recordings in TH+-labeled DNs derived from all four iPSC lines (n = 6–9 for each line) showing voltage-gated sodium and potassium currents (top row), evoked action potentials (middle), and spontaneous action potentials (bottom).
(G) Quantification of PARKIN abundance in DNs from WT, PARKIN−/−, and DJ-1−/− lines using AQUA peptides.
(H) Western blot of WT, PARKIN−/−, and ATP13A2−/− lines using PARKIN antibody and GAPDH as a control, at three time points, indicated as pluripotent at d0, NPC at d12, midbrain DN at d75, and mouse whole-brain lysate as control.
(I) Scree plot showing the percentage of variances explained by each principal component.
(J) PCA plot of components 1 and 2 at d35.
(K) PCA plot of components 2 and 3 at d35.
(L) Bar chart showing normalized relative abundance of DJ1 protein, WT samples set to 1.
(M) Bar chart showing normalized relative abundance of ATP13A2 protein, WT samples set to 1. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc test (1% FDR)-Bonferroni-Holm for multiple comparisons.