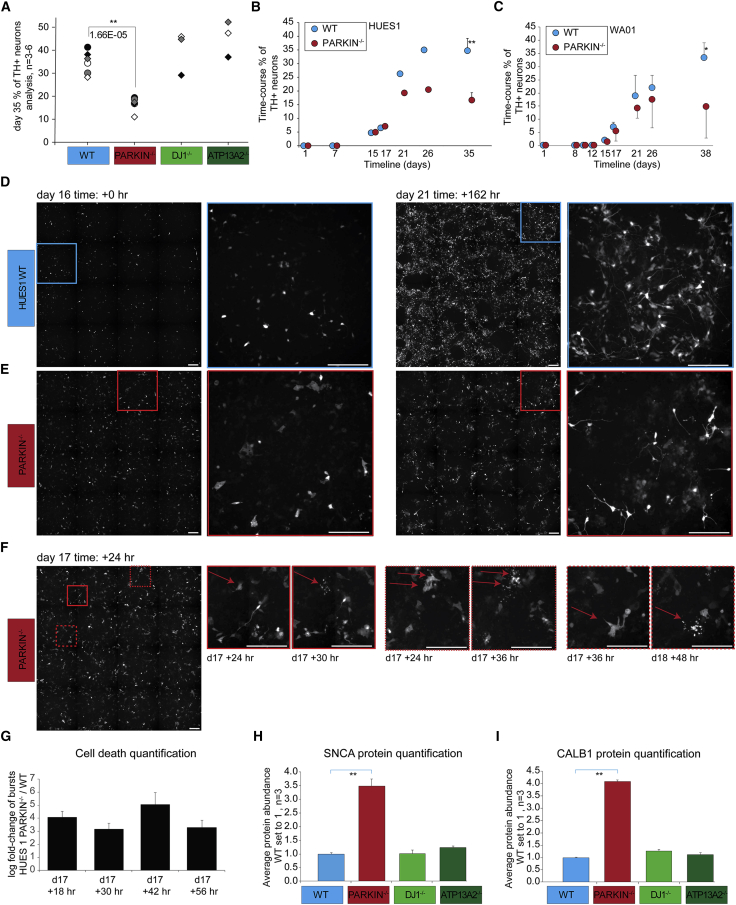
Figure 4.
Quantification of Cell Death Events in TH+ DNs
(A) Dissociated spheres were analyzed via flow cytometry, TH quantification in isogenic HUES1 lines at d35 showing decreased numbers of TH+ cells in the PARKIN−/− line. Statistical significance p value derived from one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Holm multiple comparison test (n = 6, 6, 3, and 3 independent differentiation experiments).
(B) TH quantification in WT and PARKIN−/− isogenic lines in a time course experiment in HUES1 line (n = 1 except d35 n = 6).
(C) TH quantification in WT and PARKIN−/− isogenic lines in a time course experiment in WA01 line (d0–d21, WT, n = 3 differentiation replicates; PARKIN−/−, n = 3 independent clones; d26–d38, WT, n = 4 differentiation replicates; PARKIN−/−, n = 5 or 3 independent clones, 2 differentiation replicates; d38, ∗p < 0.05, unpaired two-sided t test).
(D–F) Nikon Biostation CT live cell fluorescence imaging of TH:TdTomato expression during differentiation of WT and PARKIN−/− lines after dissociation at d15. Image acquisition starts 24 h post plating. Images were acquired every 6 h, time points indicated. Squares depict areas of interest that are shown in higher magnification. (D) WT cell line. (E) PARKIN−/− cell line. (F) Representative images of cell death events in the PARKIN−/− cell line. Zoomed images with red arrows indicating cells of interest before and after cell death.
(G) Cell death quantification of burst events in WT and PARKIN−/− cell lines at the indicated time points, shown as log2 fold change between PARKIN−/− and WT cell lines (n = 3 wells per cell line). ∗p < 0.05, unpaired two-sided t test.
(H) Bar chart showing normalized relative abundance of SNCA protein across all samples, WT samples set to 1.
(I) Bar chart showing normalized relative abundance of CALB1 protein across all samples. WT samples set to 1. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc test (1% FDR) Bonferroni-Holm for multiple comparisons.