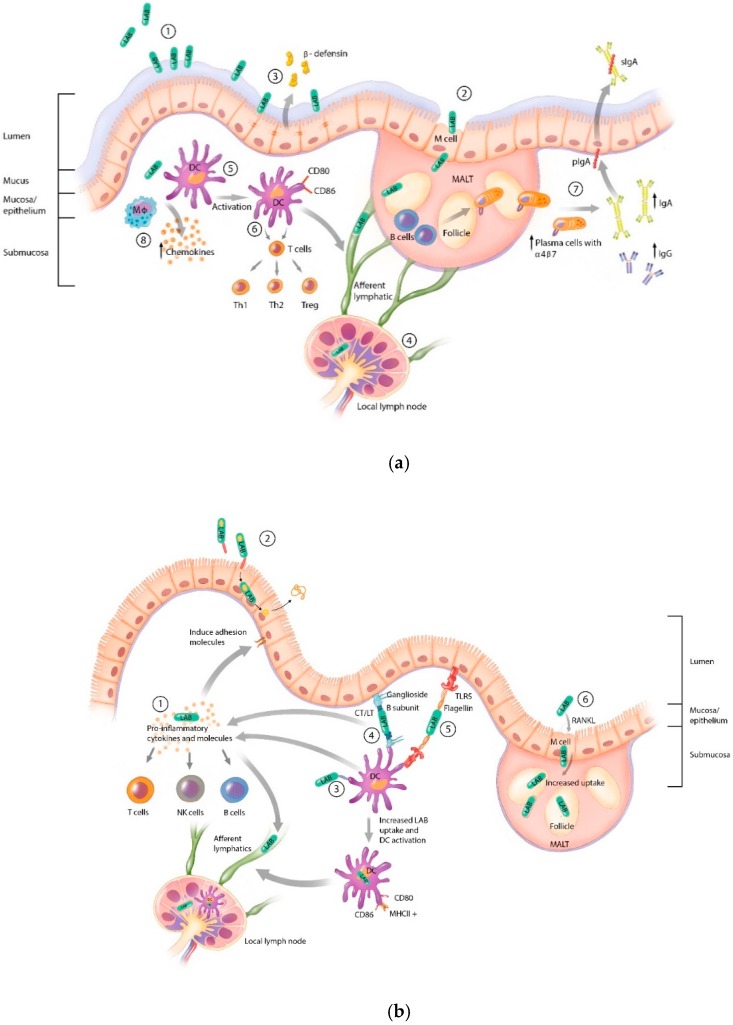
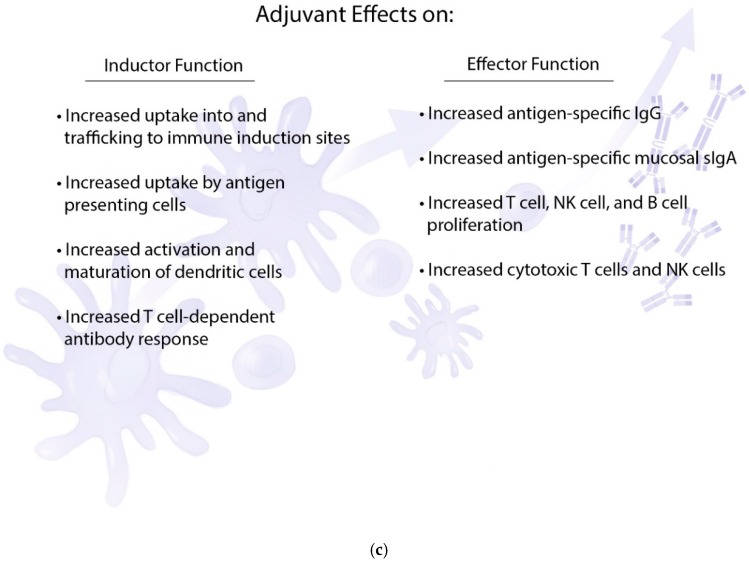
Figure 1.
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) interactions with the mucosa and mucosal immune system. (a) Endogenous LAB mucosal interactions. LAB possess the ability to bind to mucus (1), epithelial cells, and microfold (M) cells (2) allowing for uptake into mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) and trafficking to local lymph nodes (4) [24,25,26]. The interactions of LAB with the epithelium can induce epithelial defenses such as the secretion of β-defensin (3) [27,28]. LAB can activate macrophages (8) and dendritic cells (DCs) (5), which can traffic phagocytosed LAB to local immune induction sites (4) [29,30,31,32]. LAB also induce effector immune responses such as polarization of naïve T cells to Th1, Th2, and Treg cells (6) and humoral responses such as B cell proliferation, class switching to IgG and IgA, induction of long-lived plasma cells, and induction of the mucosal homing integrin α4β7 (7) [33,34]. (b) LAB mucosal adjuvant strategies. (1) LAB secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-12, IL-1β, and IL-2 activates T cells, NK cells, and B cells, induces epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression, and promotes trafficking of LAB to local lymph nodes. (2) LAB surface expression of the epithelial cell adhesion molecules InlA and/or FnBPA promotes binding and uptake of LAB by epithelial cells, delivery of eukaryotic expression plasmid, and secretion of protein. (3) LAB surface expression of DC-binding peptides results in targeting, increased uptake, and activation of DCs as well as trafficking to local immune induction sites. (4) Surface expression of LT or CT B subunit results in LAB binding to gangliosides on the surface of epithelial cells and DCs. Co-delivery of full toxins or CT/LT A subunit results in a pro-inflammatory response. (5) Surface-expressed flagellin, a TLR5 ligand, induces cytokine production by epithelial cells and direct activation of DCs. (6) LAB secretion of RANKL results in increased M cells and uptake of LAB into MALT. (c) Review of the effects of adjuvants on the immune response to LAB mucosal vaccination. LAB: Lactic acid bacteria; DC: Dendritic cell; Mϕ: Macrophage; MALT: Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue; pIgA: Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor; sIgA: Secretory IgA; NK cells: Natural killer cells; M cells: Microfold cells; TLR: Toll-like receptor; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; InlA: Listeria monocytogenes internalin A; FnBPA: Fibronectin-binding protein A; CT: Cholera toxin; LT: E. coli heat-labile toxin