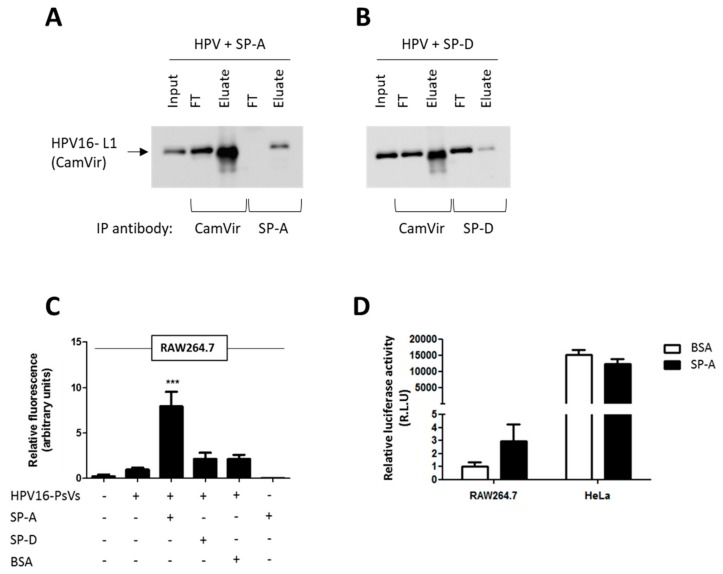
Figure 1.
Binding of HPV16-PsVs to SP-A but not SP-D results in increased viral uptake by RAW264.7 macrophages but not by HeLa cervical epithelial cells. (A,B) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments displaying the input, flow through (FT) and eluate samples of HPV16-PsVs incubated with (A) SP-A and (B) SP-D. Complexes were incubated for 1h at 4 °C, followed by precipitations with either anti-HPV16-L1 (CamVir), anti-SP-A or anti-SP-D antibodies. Western blots were performed using the CamVir antibody to detect the presence of HPV16-L1. (C) RAW264.7 cells were infected with fluorescently labelled HPV16-PsVs (pre-absorbed with recombinant proteins where indicated) for 1 h at 37 °C. Cells were washed extensively and lifted with trypsin/EDTA to remove surface-bound virions and subjected to flow cytometry to quantify viral internalization. Experiments were performed in triplicates, quantified by quadrant analysis of the dot blots of three independent experiments and presented as x-fold increase relative to the mean fluorescence intensity of cells infected with untreated HPV16-PsVs which was set as 1. Significances were calculated by means of one-way ANOVA and Tukey post-hoc tests. *** indicates statistical significance between uptake of HPV16-PsVs in the presence of SP-A as compared to the other tested conditions (*** = p < 0.001). (D) RAW264.7 and HeLa were infected with HPV16-PsVs encapsidating the firefly luciferase reporter plasmid pGL3-control for 48 h. Where indicated, the viral particles were pre-absorbed with purified SP-A protein (or BSA control) before infection. Firefly luciferase activities in the cell lysates as a measure for successful infection is presented as Relative Light Units relative to RAW264.7 cells infected with untreated HPV16-PsVs which was set as 1. Bars in C and D depict mean values, with error bars showing SEM. Surfactant proteins A and D: SP-A, SP-D.