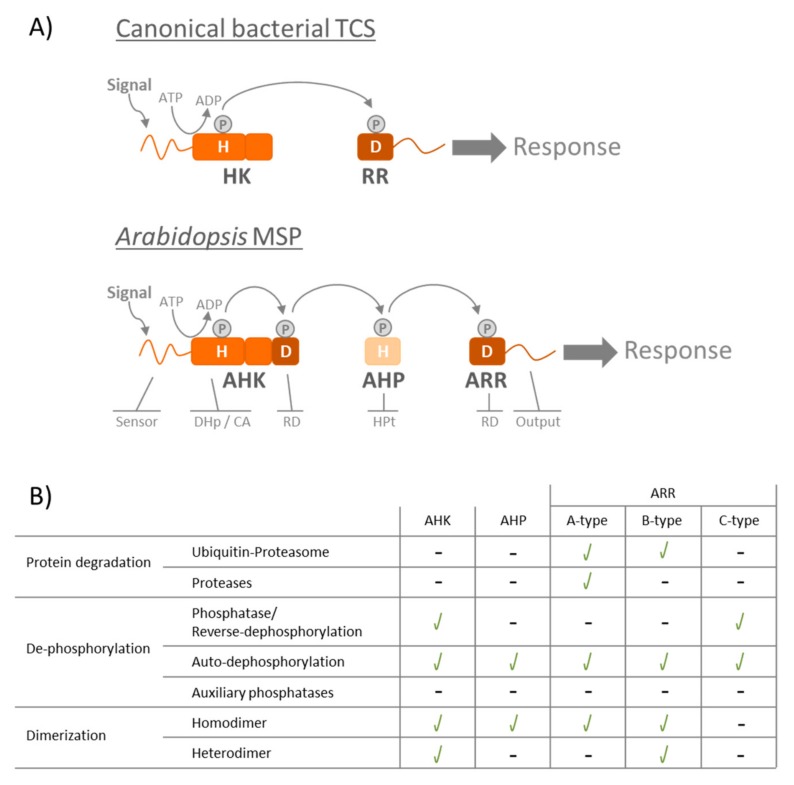
Figure 1.
(A) Diagram of a canonical bacterial two-component system (TCS) and a multistep-phosphorelay (MSP) in Arabidopsis. Upon signal perception, the histidine kinase (HK and AHK) auto-phosphorylates on a conserved His residue (H). The phosphorelay is carried out from His to Asp (H to D) to finally activate the response regulator (RR and ARR) that triggers the response. Canonical bacterial TCS only include two proteins: AHK and a RR, while Arabidopsis MSP also include His-containing phosphotransfer proteins (AHPs) that connect the phosphorelay between the AHK and the ARR. The different TCS/MSP proteins contain the following domains: Sensor: Sensor domain; DHp: Dimerization domain; CA: Catalytic domain; HPt: Histidine-containing Phosphotransfer protein; RD: Receiver Domain; Output: Output domain. (B) Summary of different processes that regulate TCS/MSP signaling. All the mechanisms depicted in this table represent different regulatory mechanisms that bacteria use to modulate TCS signaling. In this table, we describe whether these processes also occur in Arabidopsis MSP. (Green check mark): Mechanism shown to occur in Arabidopsis MSP. (-): Process that either does not take place in that specific type of protein or where there is still no research available in Arabidopsis literature.