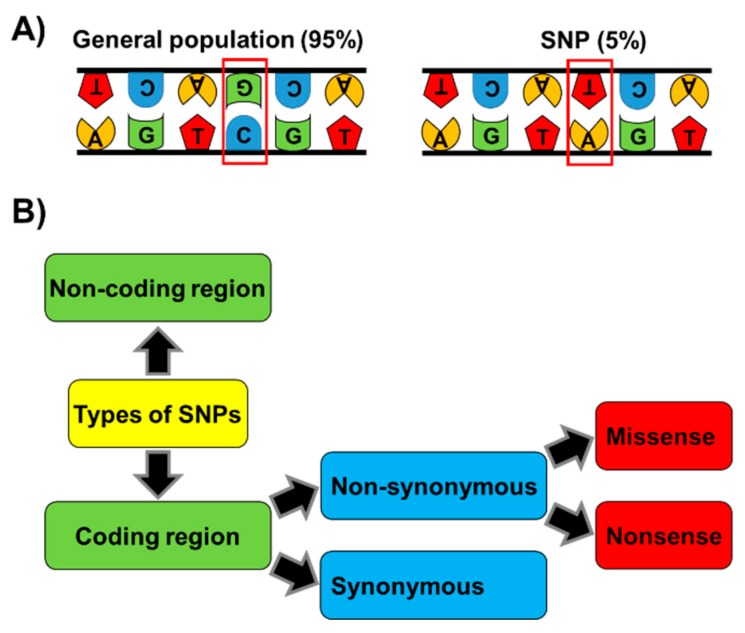
Figure 2.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). (A) An SNP is a variation on a single nucleotide which may occur at some specific point in the genome and that causes variations in DNA sequences between members of the same species. (B) Types of SNPs: DNA variation can be located in non-coding or coding regions. SNPs within a coding sequence can be synonymous if they do not produce an amino acid change (silent mutation), or non-synonymous if they affect the protein sequence. Non-synonymous changes can be divided into missense (producing an amino acid change in the protein) or nonsense (producing a truncated or longer protein).